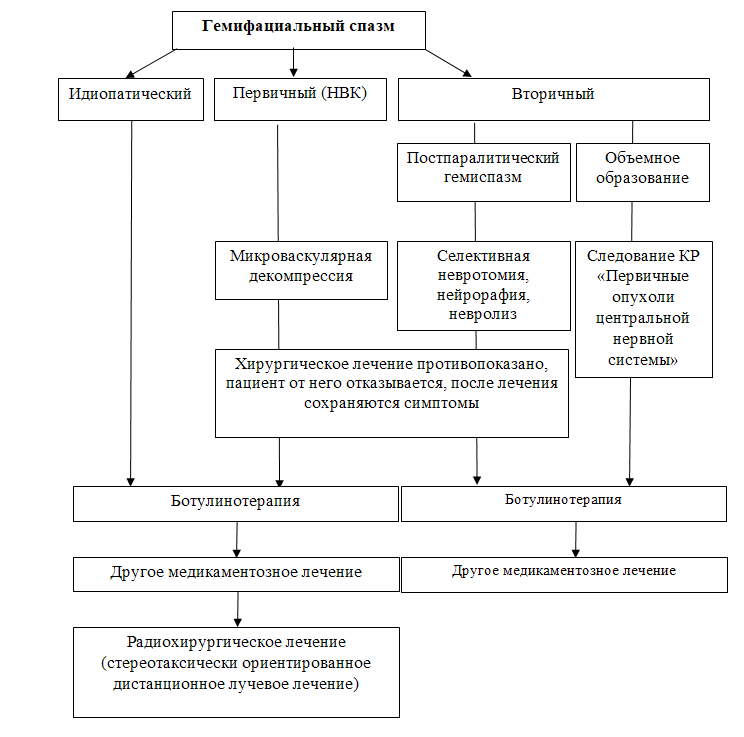
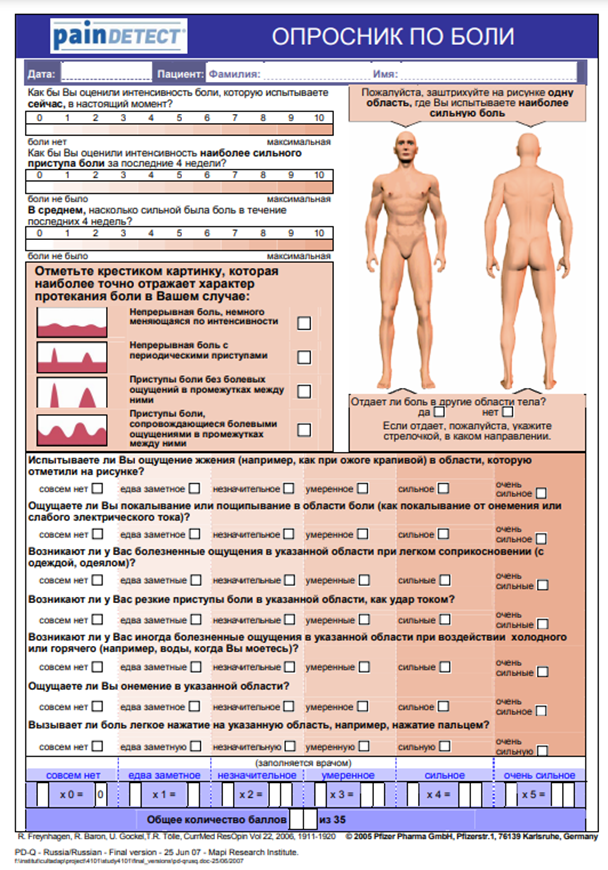
3.1. Поражения тройничного нерва
3.1.1. Тригеминальная невралгия
- Рекомендуется три подхода к лечению ТН: консервативная терапия, малоинвазивные интервенции и хирургические вмешательства [235]. Консервативное лечение включает в себя профилактическую терапию и купирование приступов острой боли [236].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Консервативная терапия
Профилактическое лечение лекарственными препаратами
- Рекомендуется профилактическая терапия всем пациентам с установленным диагнозом ТН с целью уменьшения частоты пароксизмов лицевой боли [236].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Для профилактической терапии ТН применяют противоэпилептические препараты и миорелаксанты центрального действия (таблица 13).
Таблица 13. Препараты, применяемые для профилактической терапии ТН [236,237].
Лекарственное средство | Режим дозирования | Терапевтическая суточная доза | Частые побочные эффекты |
|---|
Карбамазепин** (код АТХ - N03AF01) [236,237] | 100 мг 2 раза; увеличивать дозу препарата на 100-200 мг каждые 3 дня до 200 мг 4 раза в день | 800-1200 мг | Седация, головокружение, нечеткость зрения, тошнота, неустойчивость, вялость, диплопия, головная боль. Может вызывать гипонатриемию, кожную сыпь, панцитопению. Риск остеопороза при длительном применении. Может снизить эффективность пероральной контрацепции. |
#Окскарбазепин** (код АТХ - N03AF02) [236,237] | 150 мг 2 раза; увеличивать дозу препарата на 150-300 мг каждые 3 дня до 300 мг 4 раза в день | 1200-1800 мг | Сонливость, головокружение, диплопия, спутанность сознания, тошнота, боли в животе, головная боль, депрессия, диарея. Высокий риск гипонатриемии. Регулярное употребление увеличивает риски остеопороза. Может снизить эффективность пероральных контрацептивов. |
#Ламотриджин (код АТХ - N03AX09) [236,237] | 25 мг 1 раз в день; увеличение дозы на 25 мг каждые 2 недели; после 100 мг в сутки увеличение дозы на 25 мг каждую неделю. Кратность приема до 100 мг в сутки – возможно 1 раз в день, свыше 100 мг в сутки – 2 раза в день. | 200 мг | Нечеткость зрения, возбуждение, агрессия, неустойчивость, головокружение, тошнота, сухость во рту, бессонница, боли в суставах. Риск кожной сыпи и синдрома Стивенса-Джонсона при быстром увеличении дозы. Препарат можно отменять без титрации дозы. |
#Баклофен** (код АТХ - M03BX01) [236,237] | 5 мг 3 раза в день; каждые 3 дня увеличивать на 5 мг. | 40-80 мг | Тревога, депрессия, возбуждение, неустойчивость, головная боль, седативный эффект, тремор, кожная сыпь, нечеткость зрения, сухость во рту, боль в животе, симптомы отмены при слишком быстром прекращении. |
#Габапентин (код АТХ - N02BF01, N03AX12) [236,237] | 300 мг 1 раз в день; каждый день увеличивать дозу на 300 мг до 900 мг в сутки, затем – на 300 мг каждые 3-5 дней. | 900-3600 мг | Амнезия, спутанность сознания, головокружение, сонливость, депрессия, тошнота, нечеткость зрения, периферические отеки, отеки лица, запор, вздутие живота, увеличение веса. |
#Прегабалин** (код АТХ - N02BF02) [236,237] | 75 мг 2 раза в день | 600 мг | Спутанность сознания, сонливость, запор, нечеткость зрения, головокружение, тошнота, периферические отеки, отеки лица, повышение аппетита, увеличение веса. |
Общие рекомендации по ведению пациентов с ТН включают:
При выборе препарата следует учитывать противопоказания к применению, индивидуальную переносимость. Для улучшения переносимости лечения возможно менять препарат на дженерик с аналогичным действующим веществом и дозой;
Для оценки переносимости лечение следует начинать с монотерапии. При необходимости назначения комбинированной терапии следует назначать препараты поочередно для оценки переносимости каждого.
К препаратам первой линии лечения относят Карбамазепин** (код АТХ - N03AF01) и #Окскарбазепин** (код АТХ - N03AF02), остальные – вторая линия терапии. Препараты второй линии могут быть применены в качестве монотерапии или в сочетании с препаратами первой линии [235];
Замена одного противоэпилептического препарата на другой проводят постепенно, согласно инструкции к препарату;
При непереносимости #Баклофена** (код АТХ - M03BX01) возможно рассмотреть назначение #Клоназепама**;
При достижении ремиссии, то есть отсутствии боли в течение не менее 4 недель, следует медленно снижать дозу принимаемых препаратов согласно инструкции к ним и возможно отменить консервативное лечение полностью [238];
При рецидиве болевого синдрома следует постепенно возобновить лекарственное лечение до минимальной эффективной дозы [235];
На фоне регулярного приема противоэпилептических препаратов следует контролировать показатели крови каждые 3-6 месяцев: общий (клинический) анализ крови (тромбоциты, лейкоциты, нейтрофилы, эозинофилы), анализ крови биохимический общетерапевтический (глюкоза, ЩФ, АЛТ, АСТ, общий билирубин), электролиты сыворотки крови (натрий, калий). При необходимости – контроль ЭКГ и оценка концентрации антиконвульсантов в сыворотке крови (исследование уровня лекарственных препаратов в крови).
При отсутствии обезболивающего эффекта от любого лекарственного лечения на фоне хорошей переносимости следует рекомендовать консультацию психиатра для уточнения генеза болевого синдрома;
Для направления на нейрохирургическое лечение нет необходимости назначать каждый из приведенных препаратов. Важно своевременно информировать пациента о возможностях хирургического лечения [235].
- Рекомендуется прием Карбамазепина** (код АТХ - N03AF01) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [236].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Рекомендуется прием #Окскарбазепина** (код АТХ - N03AF02) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [238].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Рекомендуется прием #Ламотриджина (код АТХ - N03AX09) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [238].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Рекомендуется прием #Баклофена** (код АТХ - M03BX01) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [238].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Рекомендуется прием #Габапентина (код АТХ - N02BF01, N03AX12) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [238].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Рекомендуется прием #Прегабалина** (код АТХ - N02BF02) пациентам с ТН для профилактического лечения [238].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Не рекомендуется профилактическая терапия опиоидами / опиоидными препаратами (код АТХ - N02) пациентам с ТН с целью уменьшения частоты пароксизмов лицевой боли [235].
Иное профилактическое лечение.
В лечении ТН у взрослых допустимо применять ботулинотерапию и транскраниальную магнитную стимуляцию (ТМС).
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с ТН в качестве дополнительного профилактического лечения [235,239–241].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарий: применяют ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в дозе по 1,25-5 ЕД внутрикожно на расстоянии 15-20 мм друг от друга по триггерным точкам до 25-100 ЕД.
- Рекомендуется высокочастотная ритмическая транскраниальная магнитная стимуляция (ТМС) пациентам с ТН в качестве дополнительного профилактического лечения [242,243].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Купирование эпизодов острой боли при тригеминальной невралгии
- Рекомендуется применение местных анестетиков для купирования острой боли у пациентов с ТН [236,244,245].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Список препаратов представлен в таблице 14. Частое применение спрея #Лидокаина** (код АТХ - D04AB01, N01BB02) сопряжено с риском повреждения слизистой оболочки из-за наличия в составе раствора этилового спирта. Перед проведением блокады ветвей тройничного нерва необходимо выполнить кожную пробу в соответствии с инструкцией к препарату.
Таблица 14. Препараты для лечения эпизодов острой боли у взрослых с ТН.
#Лидокаин** (код АТХ - D04AB01, N01BB02) [236,244,245] | - 10% спрей для наружного и местного применения, 2 впрыскивания в носовой ход на стороне боли; - 5% гель на триггерную зону наружно; - 2% раствор #Лидокаина** (код АТХ - N01BB02) 1:80 000 #эпинефрина** (код АТХ - C01CA24) – местная инфильтрация для блокады симптомной ветви тройничного нерва; - внутривенно 1,5-5 мг/кг в течение более 1 часа. |
|---|
#ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** (код АТХ - M03AX01) [236,239,240] | 50 ЕД + 1,0 мл 0,9% физиологического раствора, подкожно в триггерные точки. |
- Не рекомендуется применение НПВП пациентам с ТН для купирование острой боли [237].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Механизм действия НПВП связан с купированием боли и воспаления путем блокирования системы ЦОГ, что является эффективным при ноцицептивной боли. Учитывая патогенез болевого синдрома при ТН, применение НПВП не эффективно. В случаях купирования боли от приема НПВП следует исключить в качестве причины болевого синдрома локальные воспалительные процессы.
Особенности лечения хронической боли, обусловленной тригеминальной невралгией, у взрослых
- Рекомендуется назначение #Амитриптилина** (код АТХ - N06AA09) пациентам с хроническим течением ТН для профилактического лечения болевого синдрома – таблица 15 [246–248]. Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
- Рекомендуется назначение #Дулоксетина (код АТХ - N06AX21) пациентам с хроническим течением ТН для профилактического лечения болевого синдрома – таблица 15 [249–251].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется назначение #Венлафаксина (код АТХ - N06AX16) пациентам с хроническим течением ТН для профилактического лечения болевого синдрома – таблица 15 [248].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Таблица 15. Препараты, применяемые для лечения хронической боли, обусловленной ТН у взрослых
Лекарственное средство | Режим дозирования | Терапевтическая суточная доза | Частые побочные эффекты |
|---|
#Амитриптилин** (код АТХ - N06AA09) [252] | прием начинают с 5-6,25 мг вечером за полтора часа до сна, затем повышают дозу на 5-6,25 мг каждые 3-5 дней | 12,5-75 мг | Седация, сухость во рту, затруднение мочеиспускания, запоры, нечеткость зрения, диплопия, повышение внутриглазного давления, нарушение памяти, тремор, аритмия. |
#Дулоксетин (код АТХ - N06AX21) [252] | прием начинают с 30 мг 1 раз в день в первой половине дня в течение 1-2 недель, затем по 60 мг 1 раз в день в первой половине дня. | 60 мг | Головокружение, нарушение сна (сонливость или бессонница), сухость во рту, тошнота, запор, повышенное потоотделение, снижение массы тела. |
#Венлафаксин (код АТХ - N06AX16) [252] | прием начинают с 18,75 мг 2 раза в день во время еды и наращивая по 18,75 мг каждые несколько дней. После достижения дозировки 75 мг в сутки можно наращивать дозу по 37,5 мг в сутки | 75-225 мг | Тошнота, снижение аппетита, запор, снижение массы тела, артериальная гипертензия, головокружение, бессонница, парестезии, тремор, нечеткость зрения, сексуальная дисфункция, потливость, высокая вероятность синдрома отмены. |
Комментарии: особенности применения антидепрессантов:
Перед началом терапии антидепрессантами важно разъяснить пациенту цели лечения, ожидаемый эффект и сроки его развития;
Следует предупредить о временных нежелательных эффектах в первые недели приема. Уведомление пациента об их транзиторном характере увеличит приверженность терапии;
Также стоит развеять основные страхи пациента, связанные с приемом антидепрессантов, расспросить все доводы «против» и предоставить аргументированный ответ.
- Рекомендуется психотерапия пациентам с хроническим течением ТН с целью снижения уровня тревоги, депрессии, катастрофизации боли, улучшения качества жизни и функциональной активности [253,254].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: среди методов психотерапии применяют следующие виды: когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) [255], биологическая обратная связь [253,254], методы релаксации [255][256], майндфулнесс [257] и другие.
Малоинвазивные пункционные вмешательства у пациентов с тригеминальной невралгией
Малоинвазивные пункционные вмешательства у пациентов с классической ТН
- Рекомендуется проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме стандартной (термической) радиочастотной абляции (СРЧА) надглазничного нерва в области надглазничного отверстия под КТ или ультразвуковым контролем пациентам с тригеминальной невралгией в проекции иннервации надглазничного нерва при недостаточной эффективности консервативной терапии [258,259].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3).
Комментарии: В поддержку данной рекомендации можно привести два ретроспективных исследования (Ren H, Xie K). Исследования показывают высокий уровень безопасности и эффективности СРЧА надглазничного нерва в диапазоне наблюдения от 24 до 36 месяцев. Учитывая, что СРЧА является деструктивной процедурой, желательно выполнять предварительную диагностическую блокаду надглазничного нерва местным анестетиком с глюкокортикостероидом для подтверждения диагноза.
- Рекомендуется проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме высоковольтажной импульсной радиочастотной абляции (ИРЧА) и/или стандартной (термической) радиочастотной абляции подглазничного нерва в области подглазничного отверстия под КТ контролем пациентам с тригеминальной невралгией в проекции иннервации подглазничного нерва при недостаточной эффективности консервативной терапии, после предварительно выполненной диагностической блокады подглазничного нерва [260–262].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2).
Комментарии: В поддержку данной рекомендации приведены 1 двойное слепое РКИ (Luo F), 1 обсервационное (Jia Y) и 1 ретроспективное исследование (Sun Z). Выборка пациентов для проведения ИРЧА и/или СРЧА основывалась, в том числе, на положительном эффекте лечебно-диагностической блокады. Исследования показывают высокий уровень безопасности и эффективности ИРЧА и/или СРЧА подглазничного нерва в диапазоне наблюдения до 2-х лет. Показана более высокая эффективность высоковольтажного (96В) ИРЧА подглазничного нерва по сравнению с 50В режимом ИРЧА. Также показана высокая эффективность комбинированного продленного (10 минут) ИРЧА в сочетании с последующей СРЧА подглазничного нерва.
Малоинвазивные пункционные вмешательства у пациентов с идиопатической и симптоматической ТН
- Рекомендуется проведение микробаллон-компрессии ганглия тройничного нерва при идиопатической или симптоматической ТН с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома в случае отсутствия регресса болевого синдрома после лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения [263].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Рекомендуется проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме стандартной (термической) радиочастотной абляции тройничного нерва при идиопатической или симптоматической ТН с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома в случае отсутствия регресса болевого синдрома после лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения [264–266].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Рекомендуется проведение глицериновой ризотомии тройничного нерва при идиопатической или симптоматической ТН с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома в случае отсутствия регресса болевого синдрома после лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения [267,268].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Хирургическое лечение
Хирургическое вмешательство рассматривается при фармакорезистентном течении болевого синдрома и нарушении качество жизни пациента. Необходимо своевременно информировать пациента о возможностях хирургического лечения и направлять пациента в нейрохирургический центр. Хирургическое лечение необходимо проводить в специализированных нейрохирургических отделениях с опытом проведения операций на головном мозге и при ТН.
- Рекомендуется нейрохирургическое лечение пациентам с фармакорезистентным течением тригеминальной невралгии или лекарственной непереносимостью терапии [269].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарий:
Фармакорезистентное течение определяется у пациентов, у которых на фоне консервативного лечения не удается достичь адекватного контроля боли или появляются выраженные побочные эффекты [235].
Нет убедительных данных о критериях фармакорезистентности и необходимого времени наблюдения за пациентами [194].
От 25 до 40% пациентов выбирают хирургическое лечение в течении 2-х лет с момента появления симптомов заболевания [236].
Во многом успех хирургического лечения зависит от точности установления диагноза и полноценного технического проведения оперативного лечения.
Хирургическое лечение пациентов с классической ТН
- Рекомендуется проведение декомпрессии корешка черепно-мозгового нерва (тройничного) пациентам с классической тригеминальной невралгией с целью устранения нейроваскулярного конфликта при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [270,271].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3).
Комментарий: условием выбора метода микроваскулярной декомпрессии корешка тройничного нерва является визуализация нейроваскулярного конфликта со структурными изменениями кореша тройничного нерва (дистопия, атрофия) на МРТ головного мозга [1]. Несмотря на публикации с успешными результатами, у пациентов старше 75 лет микроваскулярную декомпрессию необходимо рассматривать индивидуально, учитывая соматический статус пациента и риски оперативного лечения. Основным хирургическим доступом является ретросигмоидный субокципитальный. Среди видов декомпрессии распространена методика интерпозиции, а при возможности выполнения проводится транспозиция компримирующего сосуда. По данным литературы, преимуществ выполнения транспозиции нет [272]. При отказе пациента от микроваскулярной декомпрессии корешка тройничного нерва возможно проведение других нейрохирургических операций [273].
- Рекомендуется проведение стереотаксической операции на головном мозге (стереотаксической радиохирургии цистернальной порции корешка тройничного нерва с подведением максимальной дозы до 90 Гр) пациентам с классической ТН при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии и в случае невозможности проведения декомпрессии корешка тройничного нерва, в том числе при отказе пациента от хирургического лечения [274].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарий: предпочтительным является облучение на аппарате «Гамма-нож», также допустимо проведение лечения на линейных ускорителях с возможностью проведения стереотаксической радиохирургии с максимальной дозой на цистернальную порцию корешка тройничного нерва 70-90 Гр. Повторную стереотаксическую радиохирургию возможно выполнять не ранее, чем через 1 год после предыдущей.
- Рекомендуется использование имплантируемого нейростимулятора пациентам с классической тригеминальной невралгией с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома в случае отсутствия регресса боли после консервативного и/или хирургического лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения [275].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарий: обязательным условием перед имплантацией нейростимулятора для стимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагают имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
Хирургическое лечение пациентов с идиопатической ТН
- Рекомендуется проведение стереотаксической операции на головном мозге (стереотаксической радиохирургии цистернальной порции корешка тройничного нерва с подведением максимальной дозы до 90 Гр) пациентам с идиопатической ТН с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [274].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Рекомендуется проведение ризотомии (микрохирургической частичной (сенсорной) ризотомии) корешка тройничного нерва при идиопатической ТН с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [264–266].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3).
- Рекомендуется имплантация нейростимулятора пациентам с идиопатической тригеминальной невралгией с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [275].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарий: обязательным условием перед имплантацией нейростимулятора для стимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагается имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
Хирургическое лечение пациентов с ТН, связанной с рассеянным склерозом
- Рекомендуется проведение стереотаксической операции на головном мозге (стереотаксической радиохирургии) пациентам с ТН, связанной с рассеянным склерозом, с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [276,277].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3).
Комментарий:
Наиболее безопасной мишенью воздействия является цистернальная порция корешка тройничного нерва с подведением максимальной дозы до 90 Гр;
Возможно проведение медиальной таламотомии с помощью стереотаксической радиохирургии или фокусированного ультразвука у пациентов с ТН на фоне рассеянного склероза при неэффективности стереотаксической радиохирургии цистернальной порции корешка тройничного нерва.
- Рекомендуется проведение ризотомии (микрохирургической частичной (сенсорной) ризотомии) корешка тройничного нерва пациентам с ТН, связанной с рассеянным склерозом, с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [278].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Рекомендуется проведение декомпрессии корешка черепно-мозгового нерва (тройничного) пациентам с ТН, связанной с рассеянным склерозом, при наличии нейроваскулярного конфликта с признаками структурных нарушений корешка (дистопия, атрофия) на МРТ головного мозга с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [278].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарий: нет убедительных сравнительных данных о преимуществе какого-либо из методов хирургического лечения. Следует информировать пациентов о всех возможных методах хирургического лечения и их особенностях. Учитывая эквивалентную эффективность всех методов хирургического лечения, частоту рецидивов, безопаснее проводить стереотаксическую радиохирургию или малоинвазивные пункционные вмешательства [278].
- Рекомендуется имплантация нейростимулятора пациентам с тригеминальной невралгией, связанной с РС, с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [275].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарий: обязательным условием перед имплантацией нейростимулятора для стимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагается имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
Хирургическое лечение пациентов с симптоматической ТН
- Рекомендуется нейрохирургическое лечение при вторичной тригеминальной невралгии с целью устранения непосредственной причины заболевания [279,280].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарий: целесообразно выполнять хирургическое лечение, направленное на лечение основного заболевания (например, удаление опухоли) с декомпрессией корешка тройничного нерва от компримирующих факторов.
- Рекомендуется проведение стереотаксической операции на головном мозге (стереотаксической радиохирургии цистернальной порции корешка тройничного нерва с подведением максимальной дозы до 90 Гр) пациентам с симптоматической ТН в случае отсутствия регресса болевого синдрома после лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения [281].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Рекомендуется проведение ризотомии (микрохирургической частичной (сенсорной) ризотомии) корешка тройничного нерва пациентам с симптоматической ТН в случае отсутствия регресса болевого синдрома после лечения основного заболевания или при невозможности проведения такого лечения, а также при неэффективности других методов лечения болевого синдрома (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [235].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарий: нет убедительных сравнительных данных, демонстрирующих преимущество какого-либо одного метода деструкции [235].
- Рекомендуется имплантация нейростимулятора пациентам с симптоматической тригеминальной невралгией с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [275].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарий: обязательным условием перед имплантацией нейростимулятора для стимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагается имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
3.1.2. Атипичная лицевая боль
Консервативное лечение
Персистирующая идиопатическая лицевая боль
- Рекомендуется пациентам с ПИЛБ трициклические антидепрессанты (#амитриптилин**,Код АТХ: N06AA09) с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома и снижения уровня тревоги – таблица 16 [282].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Терапию начинают с минимальной дозы с приемом на ночь, так как даже минимальная доза трициклических антидепрессантов показывает свою эффективность, и наращивают с постепенной титрацией до средней терапевтической дозы согласно инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата [282].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с ПИЛБ #венлафаксин (код АТХ: N06AX16) при наличии противопоказаний, плохой переносимости или недостаточной эффективности трициклических антидепрессантов – таблица 16 [283].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
- Рекомендуется пациентам с ПИЛБ #флуоксетин** (код АТХ: N06AB03) при наличии противопоказаний, плохой переносимости или недостаточной эффективности трициклических антидепрессантов и #венлафаксина (код АТХ: N06AX16) – таблица 16 [20,26,108].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Таблица 16. Препараты для лечения ПИЛБ
Лекарственное средство | Режим дозирования | Терапевтическая суточная доза | Частые побочные эффекты |
|---|
#Амитриптилин** Код АТХ: N06AA09 [282] | 6,25-12,5 мг вечером 1 раз в сутки; увеличивать дозу препарата на 6,25-12,5 мг каждые 3-14 дней. | 10-75 мг | Седация, сухость во рту, затруднение мочеиспускания, запоры, нечеткость зрения, диплопия, повышение внутриглазного давления, нарушение памяти, тремор, аритмия. |
#Флуоксетин** код АТХ: N06AB03 [20] | 20 мг 1 раз в сутки | 20 мг | Головокружение, нарушение сна (сонливость или бессонница), сухость во рту, тошнота, запор, повышенное потоотделение, снижение массы тела, снижение либидо |
#Венлафаксин код АТХ: N06AX16 [20] | в неврологии и общей практике допустимо медленно титровать препарат: 18,75 мг 2 раза в день во время еды, наращивать по 18,75 каждые несколько дней [252] | 75 мг | Тошнота, снижение аппетита, запор, снижение массы тела, артериальная гипертензия, головокружение, бессонница, парестезии, тремор, нечеткость зрения, сексуальная дисфункция, потливость, высокая вероятность синдрома отмены. |
Комментарии: особенности применения антидепрессантов:
Перед началом терапии антидепрессантами важно разъяснить пациенту цели лечения, ожидаемый эффект и сроки его развития;
Следует предупредить о временных нежелательных эффектах в первые недели приема. Уведомление пациента об их транзиторном характере увеличит приверженность терапии;
Также стоит развеять основные страхи пациента, связанные с приемом антидепрессантов, расспросить все доводы «против» и предоставить аргументированный ответ.
- Рекомендуется пациентам с ПИЛБ габапентин (код АТХ: N02BF01) или прегабалин** (код АТХ: N02BF02) при неэффективности или непереносимости антидепрессантов – таблица 17 [20,26,108].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Таблица 17. Препараты для лечения ПИЛБ
Габапентин код АТХ: N02BF01 | 300 мг 1 раз в день; каждый день увеличивать дозу на 300 мг до 900 мг в сутки, затем – на 300 мг каждые 3-5 дней. | 900-3600 мг | Амнезия, спутанность сознания, головокружение, сонливость, депрессия, тошнота, нечеткость зрения, периферические отеки, отеки лица, запор, вздутие живота, увеличение веса. |
|---|
Прегабалин** код АТХ: N02BF02 | 75 мг 2 раза в день | 600 мг | Спутанность сознания, сонливость, запор, нечеткость зрения, головокружение, тошнота, периферические отеки, отеки лица, повышение аппетита, увеличение веса. |
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с пациентам с ПИЛБ при недостаточной эффективности медикаментозной терапии [284].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: применяют ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в область боли и окружающие ткани.
Синдром пылающего рта
- Рекомендуется пациентам с СПР трициклические антидепрессанты (#амитриптилин** (Код АТХ: N06AA09)) с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома и снижения уровня тревоги [282].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Терапию начинают с минимальной дозы с приемом на ночь, так как даже минимальная доза трициклических антидепрессантов показывает свою эффективность, и наращивают с постепенной титрацией до средней терапевтической дозы согласно инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата (средняя суточная доза 10-50 мг).[282].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с СПР габапентин (код АТХ: N02BF01) с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома [285,286].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется пациентам с СПР #альфа-липоевая кислота (тиоктовая кислота) с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома [285,286].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: рекомендуемая суточная доза препарата 600 мг. Одно из исследований продемонстрировало более высокую эффективность при совместном применении #альфа-липоевой кислоты с габапентином (код АТХ: N02BF01) [285–287].
Миофасциальная орофациальная боль связанная с мышечным спазмом
- Рекомендуется пациентам с МОБСМС нестероидные противовоспалительные и противоревматические препараты (НПВП) с целью снижения интенсивности острого болевого синдрома [288,289]. Предпочтительнее использование пероральных форм НПВП, поскольку парентеральное применение не имеет преимуществ в отношении эффективности, но существенно уступает в безопасности [290].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: При выборе НПВП необходимо принимать во внимание наличие и характер факторов риска нежелательных явлений, сопутствующих заболеваний, взаимодействие с другими лекарственными средствами. НПВП не комбинируют друг с другом, не применяют длительно (желательно ограничиться 10–14 днями лечения), что существенно снижает риск развития осложнений со стороны ЖКТ, сердечно-сосудистой и других систем. НПВП противопоказаны при эрозивно-язвенных поражениях ЖКТ, особенно в стадии обострения, выраженных нарушениях функции печени и почек, индивидуальной непереносимости, беременности, выраженной сердечной недостаточности. У пациентов с риском осложнений со стороны ЖКТ рекомендуется использовать НПВП с минимальным риском таких осложнений, в низких дозах и непродолжительное время и(или) рассмотреть возможность гастропротекции для профилактики таких осложнений. При выборе конкретного НПВП необходимо свериться с инструкцией по медицинскому применению на предмет наличия соответствующего показания и отсутствия противопоказаний [288–293].
- Рекомендуется пациентам при хронической МОБСМС трициклические антидепрессанты (#амитриптилин**, rод АТХ: N06AA09) с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома и снижения уровня тревоги [282][289].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Терапию начинают с минимальной дозы с приемом на ночь (10 мг в сутки), так как даже минимальная доза трициклических антидепрессантов показывает свою эффективность, и наращивают с постепенной титрацией до средней терапевтической дозы согласно инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата (до 150 мг в сутки) [282].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с МОБСМС #габапентин (код АТХ: N02BF01) при неэффективности или непереносимости антидепрессантов [294].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Терапию начинают с дозы 300 мг и увеличивают на 300 мг каждые 3 дня до максимальной 4200 мг.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с МОБСМС в заинтересованные мышцы для их расслабления [295–297].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарий: применяют ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** внутримышечно в заинтересованные мышцы.
Иное лечение
Персистирующая идиопатическая лицевая боль
- Рекомендуется пациентам c ПИЛБ когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) для осознания пациентом своего состояния, уменьшения катастрофизации боли, формирования позитивных стратегий преодоления боли и эмоционального стресса [298].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: Поведенческая терапия рекомендована для пациентов с персистирующей идиопатической лицевой болью, так позволяет снизить уровень тревоги и обрести реалистичную самооценку для лучшей копинг-стратегии в преодолении боли [20,298].
Синдром пылающего рта
- Рекомендуется пациентам c СПР когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) и психотерапия для осознания пациентом своего состояния, уменьшения катастрофизации боли, формирования позитивных стратегий преодоления боли и эмоционального стресса [299,300].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Миофасциальная орофациальная боль связанная с мышечным спазмом
- Рекомендуется пациентам c МОБСМС нейропсихологическая реабилитация с помощью биологической обратной связи (БОС) с целью обучения психологическому и мышечному расслаблению [301].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
- Рекомендуется пациентам c МОБСМС когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) для осознания пациентом своего состояния, уменьшения катастрофизации боли, формирования позитивных стратегий преодоления боли и эмоционального стресса [302].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Интервенционное лечение
Персистирующая идиопатическая лицевая боль
- Рекомендуется пациентам с ПИЛБ при недостаточной эффективности медикаментозной терапии радиочастотная абляция периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме импульсной РЧА крылонебного узла после предварительного положительного результата блокады крылонебного узла [303].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: в первую очередь следует проводить блокаду крылонебного узла с использованием подскулового доступа. Если после блокады достигается адекватное, но временное облегчение, следует рассмотреть возможность проведения импульсной РЧА крылонёбного узла [303].
3.1.3. Другие поражения тройничного нерва, поражение тройничного нерва неуточненное
Консервативное лечение
- Рекомендуется назначение противоэпилептических препаратов (габапентин (код АТХ - N02BF01, N03AX12), прегабалин** (код АТХ - N02BF02)) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью в качестве монотерапии или комбинации с препаратами других групп с целью уменьшения выраженности болевого синдрома – таблица 18 [304–307].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Таблица 18. Препараты для лечения тригеминальной нейропатической боли.
Лекарственное средство | Режим дозирования | Терапевтическая суточная доза | Частые побочные эффекты |
|---|
Габапентин (код АТХ - N02BF01, N03AX12) | 300 мг 1 раз в день; каждый день увеличивать дозу на 300 мг до 900 мг в сутки, затем – на 300 мг каждые 3-5 дней. | 900-3600 мг | Амнезия, спутанность сознания, головокружение, сонливость, депрессия, тошнота, нечеткость зрения, периферические отеки, отеки лица, запор, вздутие живота, увеличение веса. |
Прегабалин** (код АТХ - N02BF02) | 75 мг 2 раза в день | 600 мг | Спутанность сознания, сонливость, запор, нечеткость зрения, головокружение, тошнота, периферические отеки, отеки лица, повышение аппетита, увеличение веса. |
- Рекомендуется назначение #окскарбазепина** (код АТХ - N03AF02) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью в качестве монотерапии или комбинации с препаратами других групп с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома [308].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: начальная доза препарата составляет 300 мг в сутки с постепенным увеличением на 300 мг каждые 3 дня до 1800 мг в сутки в два приема.
- Рекомендуется назначение антидепрессантов (#амитриптилин** (код АТХ - N06AA09), #дулоксетин (код АТХ - N06AX21), #венлафаксин (код АТХ - N06AX16)) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью в качестве монотерапии или комбинации с препаратами других групп с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома – таблица 19 [248–250,309–312].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
- Рекомендуется назначение #Амитриптилина** (код АТХ - N06AA09) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома [309,310].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется назначение #Дулоксетина (код АТХ - N06AX21) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома [249,250].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется назначение #Венлафаксина (код АТХ - N06AX16) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома [248,311,312].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Таблица 19. Антидепрессанты для лечения тригеминальной нейропатической боли
Лекарственное средство | Режим дозирования | Терапевтическая суточная доза | Частые побочные эффекты |
|---|
#Амитриптилин** (код АТХ - N06AA09) [310] | в неврологии и общей практике при иных, чем депрессия расстройствах, препарат назначают с 5-6,25 мг вечером за полтора часа до сна, затем повышая дозу на 5-6,25 мг каждые 3-5 дней [252] | 75 мг | Седация, сухость во рту, затруднение мочеиспускания, запоры, нечеткость зрения, диплопия, повышение внутриглазного давления, нарушение памяти, тремор, аритмия. |
#Дулоксетин (код АТХ - N06AX21) [249,250] | 30 мг 1 раз в день в первой половине дня в течение 1-2 недель, затем по 60 мг 1 раз в день в первой половине дня. | 60 мг | Головокружение, нарушение сна (сонливость или бессонница), сухость во рту, тошнота, запор, повышенное потоотделение, снижение массы тела. |
#Венлафаксин (код АТХ - N06AX16) [248,311,312] | 9,375-18,75 мг 2 раза в день через равные временные интервалы; увеличение дозы на 9,375-18,75 мг каждые 3-7 дней. | 75-225 мг | Тошнота, снижение аппетита, запор, снижение массы тела, артериальная гипертензия, головокружение, бессонница, парестезии, тремор, нечеткость зрения, сексуальная дисфункция, потливость, высокая вероятность синдрома отмены. |
Комментарии: особенности применения антидепрессантов:
Перед началом терапии антидепрессантами важно разъяснить пациенту цели лечения, ожидаемый эффект и сроки его развития;
Следует предупредить о временных нежелательных эффектах в первые недели приема. Уведомление пациента об их транзиторном характере увеличит приверженность терапии;
Также стоит развеять основные страхи пациента, связанные с приемом антидепрессантов, расспросить все доводы «против» и предоставить аргументированный ответ.
- Рекомендуется местное применение пластыря с содержанием в его составе 5% #лидокаина (код АТХ - N01BB02) на область боли пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома в качестве дополнительной терапии [312,313].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется местное применение геля с содержанием в ее составе #лидокаина (код АТХ - A01AD11) на область боли пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома в качестве дополнительной терапии [314].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется назначение опиоидных анальгетиков (содержат в составе одно из веществ: тапентадол** (код АТХ - N02AX06), налоксон+оксикодон** (код АТХ - N02AA05), трамадол** (код АТХ - N02AX02), морфин** (код АТХ - N02AA01) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома – таблица 20 [315–320].
Таблица 20. Уровень убедительности рекомендаций и уровень достоверности доказательств опиоидных анальгетиков в лечении нейропатической боли.
Лекарственное вещество | УУР | УДД |
|---|
Тапентадол (код АТХ - N02AX06) | В | 2 |
Налоксон+Оксикодон** (код АТХ - N02AA05) | А | 1 |
Трамадол** (код АТХ - N02AX02) | А | 1 |
Морфин** (код АТХ - N02AA01) | А | 1 |
Комментарии: Особенности применения опиоидных анальгетиков:
Препараты данной группы относят к терапии третьей линии в связи с риском развития лекарственной зависимости и нежелательных явлений на фоне длительного применения;
При выборе препарата следует учесть опыт применения опиоидных анальгетиков в анамнезе, наличие в анамнезе лекарственной зависимости;
Доза препаратов подбирается индивидуально, основываясь на инструкции к препарату, переносимости и эффективности, наличии у пациента сопутствующей онкологической боли.
- Рекомендуется назначение #Альфа-липоевой кислоты** (тиоктовой кислоты) (код АТХ - A16AX01) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью в качестве дополнительной терапии с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома [321].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: рекомендуемая суточная доза 600 мг.
Иное лечение
- Рекомендуется психотерапия пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения уровня тревоги, депрессии, катастрофизации боли, улучшения качества жизни и функциональной активности [253,322].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: среди методов психотерапии применяют следующие виды: когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) [255], биологическая обратная связь [253], методы релаксации [255,256], майндфулнесс [257] и другие.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома в качестве дополнительного лечения [242,323,324].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарий: применяют ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в зоне боли.
- Рекомендуется высокочастотная ритмическая транскраниальная магнитная стимуляция (ТМС) пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома в качестве дополнительного лечения. Частота стимуляции 5-20 Гц, количество сеансов 5-10, область стимуляции – первичная моторная или дорсо-латеральная префронтальная кора [242,243,325].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
- Рекомендуется назначение гипербарической оксигенации (ГБО) при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с тригеминальной постгерпетической невралгией и посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью уменьшения выраженности аллодинии и зуда [326–328].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: рекомендовано проведение не менее 10 сеансов ГБО.
Особенности лечения посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической боли, вызванной радиационным поражением
- Рекомендуется назначение антиоксидантов (#альфа-токоферола ацетат (код АТХ - A11HA03)) пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью, вызванной радиационным поражением, с целью лечения клинически значимых лучевых изменений [329–332].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: на фоне приема высоких доз #альфа-токоферола ацетата (код АТХ - A11HA03) (свыше 400 мг в сутки) следует проводить профилактическое лечение дефицита ретинола ацетата** (код АТХ - D10AD02, R01AX02, S01XA02, A11CA01) – рекомендовано одновременное назначение ретинола** с #альфа-токоферола ацетатом**(код АТХ - A11HA03).
- Рекомендуется назначение #пентоксифиллина** (код АТХ - C04AD03) пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью, вызванной радиационным поражением, с целью лечения клинически значимых лучевых изменений [330–332]. Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: рекомендуемая доза препарата составляет 400 мг 2 раза в день в течение 4-6 недель.
- Рекомендуется назначение гипербарической оксигенации (ГБО) при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью, вызванной радиационным поражением, с целью лечения клинически значимых лучевых изменений [333].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: рекомендовано проведение не менее 10 сеансов ГБО.
- Рекомендуется назначение глюкокортикостероидов (ГКС) пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью, вызванной радиационным поражением, с целью лечения клинически значимых лучевых изменений [334].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: в лечении клинически значимой посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической боли, вызванной радиационным поражением, может быть применен как #дексаметазон** (код АТХ - H02AB02), так и #преднизолон** (код АТХ - H02AB06). Решение о назначении ГКС должно быть принято с учетом пользы и риска для здоровья пациента, сопутствующих заболеваний, возможных осложнений терапии ГКС. Начальная эффективная доза дексаметазона составляет не менее 8 мг в сутки (и не более 20 мг) в сутки в течение 3-5 дней с последующим постепенным уменьшением. Прием преднизолона возможен в эквивалентных дозах.
Хирургическое лечение
Малоинвазивные пункционные и хирургические вмешательства у пациентов с тригеминальной нейропатической болью
При различных видах фармакорезистентной тригеминальной нейропатической боли рассматриваются следующие методы лечения:
Проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев;
Имплантация нейростимулятора;
Тригеминальная нуклеотрактотомия.
- Рекомендуется имплантация нейростимулятора для инвазивной стимуляции прецентральной коры головного мозга пациентам с тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [335–337].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3).
Комментарий: учитывая длительность наступления эффекта от стимуляции двигательной коры, необходимость в проведении тестовой стимуляции является дискутабельным вопросом. Эффективность метода носит противоречивый характер, однако решение о проведении оперативного лечения необходимо принимать с учетом комплекса факторов: эффективности транскраниальной магнитной стимуляции, психологического состояния пациента, функционального статуса, резерва консервативных методов лечения и т.д.
Малоинвазивные пункционные и хирургические вмешательства у пациентов с тригеминальной постгерпетической невралгией
- Рекомендуется проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме высоковольтажной импульсной радиочастотной абляции (ИРЧА) или стандартной (термической) радиочастотной абляции (СРЧА) надглазничного нерва под КТ контролем пациентам с тригеминальной постгерпетической невралгией в проекции иннервации надглазничного нерва при недостаточной эффективности консервативной терапии, после предварительно выполненной диагностической блокады надглазничного нерва с применением местного анестетика с глюкортикостероидом [338,339].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарии: В поддержку данной рекомендации приводим рандомизированное исследование без плацебо контроля [338] и ретроспективное описание серии клинических случаев [339]. Исследования показывают высокий уровень безопасности и эффективности ИРЧА и СРЧА надглазничного нерва в диапазоне наблюдения до 1 года. В работе показана более высокая эффективность высоковольтажного (65В) ИРЧА надглазничного нерва по сравнению с 45В ИРЧА.
- Рекомендуется имплантация системы электростимуляции периферических нервов для инвазивной периферической стимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва пациентам с тригеминальной постгерпетической невралгией с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [275,340,341].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: обязательным условием является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагается имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
Хирургическое лечение посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической боли
- Рекомендуется имплантация нейростимулятора для инвазивной периферической электростимуляции ветвей тройничного нерва пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности/ непереносимости консервативного лечения или снижении приверженности к лекарственной терапии [275,340,342–344].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: обязательным условием является проведение тестовой инвазивной стимуляции для определения эффективности метода. При адекватном контроле над болью при тестовой периферической стимуляции пациенту предлагается имплантация системы для хронической стимуляции.
- Рекомендуется проведение тригеминальной нуклеотрактотомии пациентам с посттравматической тригеминальной нейропатической болью с целью снижения интенсивности болевого синдрома при неэффективности других методов лечения (консервативного, малоинвазивного и хирургического) [345–347].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: возможно выполнение микрохирургической или перкутанной тригеминальной нуклеотрактотомии в зависимости от количества и степени вовлечения дерматомов тройничного нерва. Несмотря на достаточно высокую эффективность метода, оперативное лечение носит определенный риск временных и стойких неврологических осложнений.
3.1.4. Тригеминальные автономные вегетативные цефалгии
Лечение кластерной головной боли состоит из лечения приступа и профилактического лечения.
Лечение приступа кластерной головной боли.
- Рекомендуется ингаляция 100% кислорода со скоростью 12 л/мин в отдельных случаях 15 л/мин в течении 20 минут при помощи маски пациентам с кластерной головной болью для купирования приступа [348–355].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств - 1)
Комментарий: Следует отдавать предпочтение маскам с клапаном для подачи кислорода, чтобы обеспечить достаточный его поток [350,351]. При отсутствии возможности проведения оксигенотерапии в домашних условиях, возможно ее проведение в условиях палат дневного стационара с возможностью проведения подачи кислорода со скоростью 12-15 л/мин в течении 20 мин.
- Рекомендуется применение селективных агонистов серотониновых 5-HT1-рецепторов (код АТХ: N02CC) пациентам с приступом кластерной головной боли с целью купирования приступа [356].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств - 1)
Комментарий: следует отдавать предпочтение золмитриптану (код АТХ: N02CC03) в дозе 5-10 мг интраназально в контрлатеральную ноздрю [357], оральные формы менее эффективны из-за более длительного развития эффекта от применения лекарства.
- Рекомендуется инстилляция спрея раствора #лидокаина (Код АТХ: N01BB02) 4 дозы в ипсилатеральную ноздрю пациенту в положении полулежа под углом 45О с поворотом головы на 30-40Ов симптомную сторону пациентам с кластерной головной болью для купирования приступа [358,359].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарий: инстилляция #лидокаина** (Код АТХ: N01BB02) может быть предложено в качестве стартовой терапии, так как не вызывает побочных эффектов, время действия составляет около 2 часов.
Профилактическое лечение кластерной головной боли
Целью профилактического лечения является предупреждение развития приступов кластерной головной боли, а также увеличения срока ремиссий заболевания.
- Рекомендуется применение #верапамила (Код АТХ:C08DA01) у пациентов с эпизодической и хронической кластерной головной болью с целью профилактики приступов и увеличения периода ремиссии [360–362].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарий: в двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании установлена эффективность #верапамила для профилактики кластерной головной боли в клинической практике следует начинать лечение с суточной дозы 240 мг (240 мг #Верапамила ретард 1 раз в день или по 80 мг #Верапамила 3 раза в день). Перед началом лечения обязательно проведение ЭКГ. Доза #верапамила увеличивается на 80 мг каждые 3-4 дня. После достижения суточной дозы 480 мг контроль ЭКГ следует выполнять каждые добавленные 160 мг [355]. Возможно постепенное увеличение дозы до 960 мг (4 таблетки по 240 мг) под наблюдением кардиолога. Как правило для эффективного лечения нужны высокие дозы, таким образом титрация #верапамила может занимать от 14 до 21 дня. В связи с длительной титрацией эффективной дозы дискутабельно применение #верапамила у пациентов с эпизодической КГБ с симптомным периодом 1-3 недели. #Верапамил достаточно хорошо переносится пациентами, из возможных побочных эффектов следует отметить утомляемость, запоры, отеки нижних конечностей. Большую опасность представляют кардиальные побочные эффекты #верапамила (отрицательный инотропный и хронотропный эффекты), также возможна брадикардия, нарушения атрио-вентрикулярной проводимости. Следует помнить о том, что кардиальные побочные эффекты #верапамила могут также развиваться у пациентов с уже подобранной дозой препарата (рекомендуется периодическое проведение ЭКГ) [360].
- Рекомендуется применение #преднизолона** (код АТХ: H02AB06) в период подбора дозы верапамила у пациентов с кластерной головной болью или у пациентов с эпизодической кластерной головной болью с продолжительностью симптомного периода до 8 недель с целью профилактического лечения [363].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарий: #Преднизолон** в дозе 100 мг внутрь в утренние часы в течении 5 дней с постепенным снижением дозы каждые 3 дня на 20 мг. По достижению дозы 10-20 мг возможно возвращение кластерной головной боли.
- Рекомендуется применение #карбоната лития (код АТХ: N05AN01) у пациентов с кластерной головной болью для профилактического лечения [362,364].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 1)
Комментарий: #Карбонат лития используется в дозе 353-900 мг. Необходимо контролировать уровень лития в плазме крови. Минимальный терапевтический уровень составляет 0,4 ммоль/л, идеальным уровнем считается 0,6-0,8 ммоль/л, не рекомендуется достигать уровня 1,2 ммоль/л. Перед началом лечения необходим лабораторный контроль. Нужно оценить уровень электролитов крови (исследование уровня натрия в крови, исследование уровня калия в крови), почечную функцию (анализ крови биохимический общетерапевтический, включая исследование уровня мочевины в крови, исследование уровня креатинина в крови, гормоны щитовидной железы (исследование уровня тиреотропного гормона (ТТГ) в крови) и прием (осмотр, консультация) врача-эндокринолога первичный, общий (клинический) анализ крови (с обязательным определением СОЭ), а затем регулярно не менее 1 раза в месяц, исследование уровня лития в крови через 12 ч после приема последней дозы, также необходима ЭКГ.
- Рекомендуется применение #мелатонина у пациентов с кластерной головной болью с целью профилактического лечения [365].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарий: В двойном слепом контролируемом исследовании установлена эффективность #мелатонина (код АТХ: N05CH01) в дозе 10 мг для профилактического лечения КГБ [365], однако в другом исследовании случай-контроль эффективность мелатонина не подтверждена [366].
- Рекомендуется применение #топирамата** (код АТХ: N03AX11) у пациентов с кластерной головной болью для профилактики приступов [367,368].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
Комментарий: рекомендуется постепенная титрация препарата, начиная с 50 мг 1 р/д с дальнейшим увеличением дозы на 25 мг 1 раз в неделю до достижения дозы 50 мг. В случае недостаточной эффективности возможно дальнейшее постепенное увеличение до дозы 100 мг. Наиболее частые побочные эффекты #топирамата** – когнитивные нарушения, снижение веса, парестезии.
Интервенционное лечение кластерной головной боли
- Рекомендовано периодически выполнять блокады раствором местного анестетика (код АТХ: N01B) с/без глюкокортикоида (код АТХ: H02AB) большого затылочного нерва для временного профилактического лечения эпизодической и хронической кластерной головной боли у пациентов с тяжелым течением кластерной головной боли до подбора оптимальной фармакотерапии [369,370].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарии: Результаты двух рандомизированных исследований указывают на эффективность периодической блокады раствором местного анестетика с/без глюкокортикоида затылочного нерва для облегчения эпизодической и хронической кластерной головной боли с ежедневными приступами. Эффект сохранялся в течение 2-4 недель, возможно повторное выполнение процедуры [369,370]. Механизм действия основан на временном подавлении тригеминально-парасимпатического рефлекса через воздействие на взаимосвязанные системы затылочного и тройничного нервов [371].
- Рекомендовано выполнять трансназальную неинвазивную блокаду крылонебного ганглия с использованием 10% #лидокаина ** (Код АТХ: N01BB02) для купирования болевого приступа при эпизодической и хронической кластерной головной боли [372].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарии: Результаты рандомизированного исследования указывают на большую эффективность трансназальной неинвазивной (с использованием ватного тампона, пропитанного раствором, введенного в носовой ход) блокады с 10% #лидокаином по сравнению с плацебо. Эффект (купирование приступа) наступал через 30-40 мин и сохранялся не менее 5 часов [372].
- Рекомендовано выполнять радиочастотную абляцию периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме импульсной радиочастотной абляции (ИРЧА) и/или стандартной (термической) радиочастотной абляции крылонебного ганглия c использованием рентген- или КТ-навигации для быстрого купирования приступа, а также профилактического лечения фармакорезистентной эпизодической кластерной головной боли [373,374].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
Комментарии: Рекомендация основана на результатах 2 ретроспективных исследований. В работе Sanders M с соавт. После применения стандартной радиочастотной абляции крылонебного ганглия было продемонстрировано полное исчезновение боли у 61% и частичное у 25% пациентов с фармакорезистентной эпизодической кластерной головной болью в течение срока наблюдения, который составлял 29 месяцев [373]. В исследовании Fang L с соавт. для той же категории пациентов была применена импульсная радиочастотная абляция крылонебного ганглия, в 85% случаев процедура была эффективна, в течение срока наблюдения продолжительностью в 17 месяцев у пациентов наблюдали увеличение периода ремиссии с 8,7 до 16,6 месяцев, а также сокращение продалжительности периода кластера с 2 до 0,5 месяцев [374].
- Рекомендовано выполнять радиочастотную абляцию периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме радиочастотной абляции крылонебного ганглия в стандартном режиме c использованием рентген-навигации для купирования приступов, а также профилактического лечения пациентов с фармакорезистентной хронической кластерной головной болью после положительного ответа (в виде временного снижения боли) на диагностическую блокаду крылонебного ганглия с применением местного анестетика [375][376].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
Комментарии: В ретроспективном исследовании Narouze S с соавт. после применения стандартной радиочастотной абляции крылонебного ганглия у пациентов с хронической кластерной головной болью было отмечено статистически значимое снижение: интенсивности боли, частоты приступов, а также нетрудоспособности, связанной с болью на протяжении 18 месяцев наблюдения после процедуры [375]. В серии клинических случаев, представленной Bendersky DC с соавторами, была продемонстрирована эффективность применения стандартной радиочастотной абляции после не успешного применения данной процедуры в импульсном режиме у пациентов с фармакорезистентной кластерной головной болью [376].
Хирургическое лечение кластерной головной боли
- Рекомендовано имплантировать постоянную систему стимуляции затылочных нервов (СЗН) для профилактического лечения пациентов с фармакорезистентной хронической кластерной головной болью [377–379].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
Комментарии: Рекомендация основана на результатах 3 когортных несравнительных исследований. В работе Miller S с соавт. после имплантации системы СЗН снижение частоты приступов на 50 и более % было достигнуто у 52,9% пациентов с фармакорезистентной хронической кластерной головной болью [377]. У больных отмечали снижение продолжительности и интенсивности болевых приступов, уменьшение использования триптанов для купирования боли, а также улучшение работоспособности и качества жизни. В исследовании Leone M [378] наблюдали за пациентами после имплантации системы СЗН в течение 6 лет и отмечали снижение частоты приступов кластерной головной боли у 66,7% пациентов. В работе Fontaine D [379] с соавторами с наблюдением после начала СЗН в течение 1 года снижение частоты приступов более чем на 30% отмечали у 64% больных, более чем на 50% - у 59% пациентов, дозировки препаратов для профилактической терапии были снижены у 40% больных, отмечено значимое улучшение у пациентов качества жизни, параметров функциональной и эмоциональной сферы.
- Рекомендовано имплантировать постоянную систему стимуляции крылонебного ганглия для купирования приступов и профилактического лечения (снижения частоты приступов) у пациентов с фармакорезистентной хронической кластерной головной болью [380–383].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарии: Рекомендация основана на результатах 2 рандомизированных сравнительных [381,382] и 1 обсервационного не сравнительного [383] исследований. В работе Schoenen J с соавт. более 70% пациентов отмечали прекращение приступов или значимое снижение их частоты после установки системы стимуляции крылонебного ганглия. В исследовании Goadsby P в группе пациентов со стимуляцией крылонебного ганглия облегчение в течение 15 минут наступало у 62,46% пациентов, в то время как в контрольной группе только у 38,87% больных, в группе со стимуляцией крылонебного ганглия пациенты также отмечали значимое снижение частоты приступов. В работе Barloese M с соавторами было показано, что после имплантации системы стимуляции крылонебного ганглия 55% пациентов с фармакорезистентной хронической кластерной головной болью отмечали более чем 50% снижение частоты приступов, у 67% значимо улучшилось качество жизни, 67% пациентов, принимавших лекарства для купирования приступов, смогли сократить их использование на 52%, а 74% пациентов смогли уменьшить дозировки или полностью прекратить прием препаратов для профилактического лечения.
Консервативное лечение
- Рекомендуется применение #индометацина (код АТХ: M01AB01) у пациентов с пароксизмальной гемикранией для лечения и профилактики приступов [384,385].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарий: Максимальная суточная доза #индометацина (код АТХ: M01AB01) составляет 250 мг.
Поскольку приступы SUNCT и SUNA очень непродолжительны, не разработаны методы лечения отдельных приступов. Целью терапии является профилактика возникновения приступов.
- Рекомендовано применение #ламотриджина (Код АТХ: N03AX09) у пациентов с SUNCT для длительного профилактического лечения SUNCT [386,387].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 4)
Комментарий: титрацию #ламотриджина следует начинать с дозы 50 мг в день и постепенно повышать, ориентируясь на реакцию и побочные эффекты. Тем не менее, лечение #ламотриджином не было столь эффективным у пациентов с SUNA.
- Рекомендуется применение #Габапентина (Код АТХ: N03AX12) у пациентов с SUNCT для профилактики приступов [388,389].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 4)
Комментарий: начальная доза 300 мг с дальнейшим увеличением на 300 мг каждые 3 дня до максимальной 4200 мг.
- Рекомендуется применение прочих противоэпилептических средств (Код АТХ: N03AX12) у пациентов с SUNA для профилактики приступов [390].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 5)
- Рекомендуется внутривенное введение #лидокаина** (Код АТХ: N01BB02) у пациентов при обострениях SUNCT, на период подбора профилактической терапии [391–393].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств - 4)
Комментарии: В одном случае сообщалось, что положительный эффект #лидокаина**, вводимого посредством внутривенной инфузии в дозе 1,3 мг/кг/час в течение 14 дней, сохранялся в течение 2 месяцев после окончания инфузии [392].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с гемикранией континуа назначение #индометацина (код АТХ: M01AB01) для лечения болевого синдрома [394].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств - 2)
Комментарий: Стандартная терапевтическая доза #индометацина составляет по 25 мг 3 раза в день в течение 5-7 дней, при неэффективности – повышение дозы до 50 мг 3 раза в день в течение 5-7 дней, при неэффективности – 75 мг 3 раза в день в течение 2 недель. Однако с учетом возможных гастроинтестинальных побочных эффектов рекомендуется начинать титрацию с низких доз.
3.2. Поражения лицевого нерва
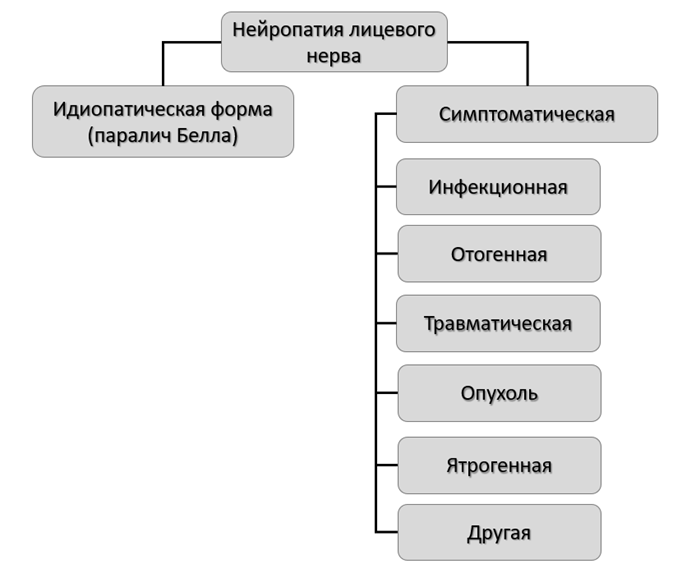
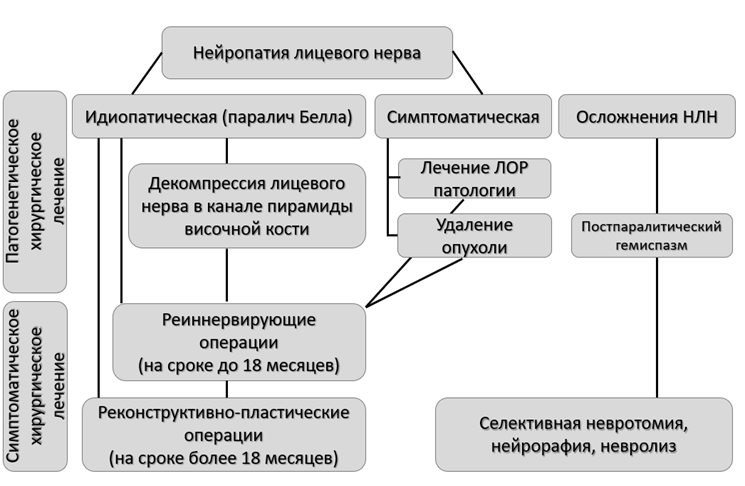
3.2.1. Нейропатия лицевого нерва
Медикаментозное лечение
При лечении пациентов с идиопатической формой НЛН (паралич Белла) большинство авторов подтверждают эффективность глюкокортикостероидной и противовирусной терапии; симптоматической - назначается лечение в зависимости от этиологии заболевания. Единичные исследования рекомендуют к использованию витамины группы В, тиоктовую кислоту. При этом, главную роль играет физическая реабилитация (Приложение Б6).
Паралич Белла
- Рекомендуется раннее назначение (оптимально – в течение первых 72 часов от дебюта симптомов) препаратов группы глюкокортикостероиды пациентам с идиопатической НЛН независимо от степени тяжести заболевания с целью уменьшения отёка и улучшения исхода заболевания [395–397].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: Лечение препаратами группы глюкокортикостероиды повышает частоту полного восстановления функции нерва на 17%, должно назначаться как можно раньше независимо от тяжести заболевания, т.к. в первые дни возможно нарастание слабости мышц [395]. Препаратами выбора являются #преднизолон** (код АТХ – H02AB06) и #метилпреднизолон** (код АТХ – H02AB04). Рекомендуемые дозы в клинической практике различаются [398]. #Преднизолон** рекомендовано назначать для перорального приема в суточной дозе 60 мг в течение первых 5 дней с постепенным снижением на 10 мг в сутки в течение следующих 5 дней [121,399–401] или 1 мг/кг веса пациента в течение 7–10 дней, а при тяжелом поражении (V-VI степень по шкале ХБ) и отсутствии противопоказаний возможно назначение 2 мг/кг веса пациента в сутки в течение 10 дней [115]. В соответствии с инструкцией к препарату всю суточную дозу принимают однократно утром в 6:00-8:00 после еды или её можно распределить на 2 приема в первой половине дня. В случаях, если начало лечения проводят до 3 дней и тяжесть НЛН выше IV степени по шкале ХБ необходимо отдать предпочтение однократному внутривенному введению #метилпреднизолона** в дозе 500 мг вместо перорального преднизолона [396,399–401]. Ежедневное интратимпанальное введение глюкокортикостероидов до 10 дней в сочетании с системной терапией может улучшить исход, однако пока данных недостаточно, необходимо проведение РКИ [402] (УДД - 1).
- Рекомендуется назначение противовирусных средств системного действия пациентам с идиопатической НЛН c целью патогенетического лечения [403–405].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: Противовирусные средства системного действия назначаются совместно с глюкокортикостеродами, поскольку согласно вирусной гипотезе идиопатическая НЛН ассоциирована с инфекцией, вызванной Herpes zoster, опоясывающим герпесом [403,404] (в качестве монотерапии не показали свою эффективность [406–408]), на ранних стадиях заболевания у пациентов с тяжёлой НЛН и/или при подтвержденной вирусной инфекции [120,121]. Препаратами выбора являются ацикловир** (код АТХ – J05AB01) и валацикловир (код АТХ – J05AB11) [115], назначение в соответствии с инструкцией по применению. В большинстве исследований рекомендованный режим дозирования для препарата ацикловир по 800 мг 5 раз в сутки, валацикловир – 1000 мг 3 раза в сутки [409].
Синдром Рамсея Ханта
- Рекомендуется раннее комбинированное назначение глюкокортикостероидов и противовирусных средств системного действия пациентам с синдромом Рамсея Ханта [410].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: Противовирусные средства системного действия назначаются совместно с глюкокортикостеродами – #преднизолон** (код АТХ – H02AB06) или #метилпреднизолон**(код АТХ – H02AB04) курсом 7 дней [115].
Болезнь Лайма (боррелиоз)
- Рекомендуется раннее назначение антибактериальных препаратов системного действия пациентам с НЛН при подозрении на бактериальную этиологию заболевания (болезнь Лайма) [411].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: «стандартная» антибактериальная терапия болезни Лайма включает доксициклин** (код АТХ - J01AA02), амоксициллин** (код АТХ - J01CA04) или цефуроксим** (код АТХ - J01DC02) в соответствии с инструкцией по применению.
- Рекомендуется при наличии болевого синдрома в мышцах назначение нестероидных противовоспалительных и противоревматических препаратов [82,412].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: целесообразно назначать ибупрофен** (код АТХ – M01AE01) в соответствии с инструкцией по применению [290,413].
- Рекомендуется назначение комплекса витаминов группы В, включая комбинации с другими препаратами, пациентам с НЛН c целью улучшения метаболических процессов в нервной системе [414,415].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Ботулинотерапия
Ботулинотерапию проводят пациентам в остром и хроническом периодах заболевания [416].
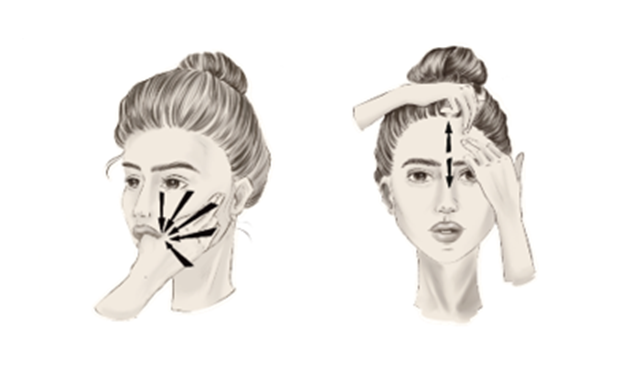
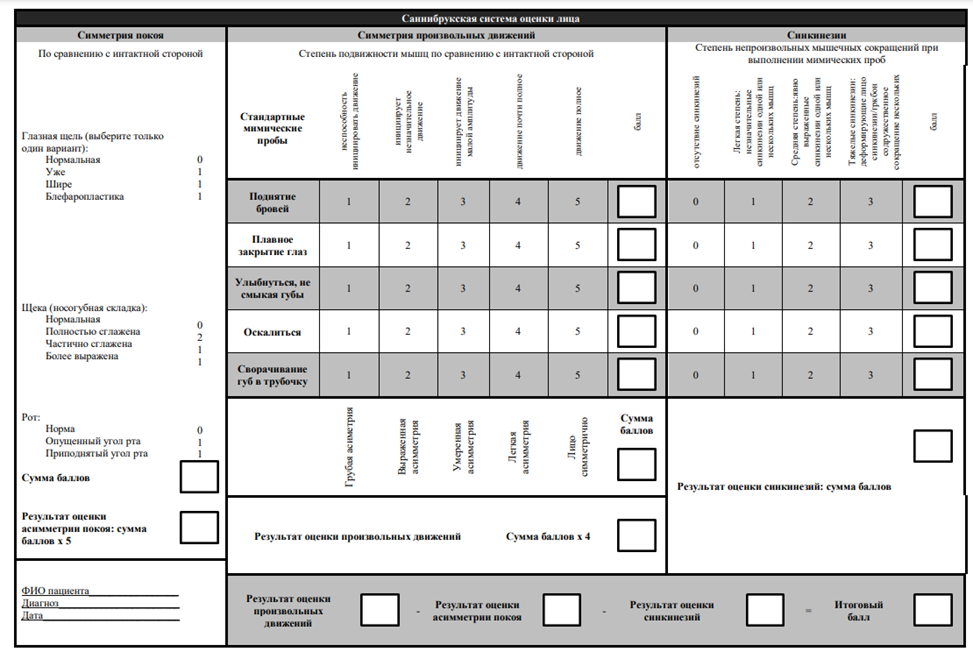
В остром периоде НЛН инъекции БТА выполняют в мышцы здоровой половины лица в случаях развития гипертонуса мышц или высокого риска его развития вследствие активной мимики, что приводит к смещению средней линии лица и ухудшает прогноз на восстановление функции. Основной целью является восстановление симметрии лица [82,417,418]. Целесообразно применение БТА в остром периоде НЛН после нейрохирургических операций [98,419].
В хроническом периоде НЛН инъекции БТА выполняют на пораженной стороне для лечения синкинезий (постпаралитического гемиспазма), при этом препарат вводят и в здоровую сторону для достижения симметрии лица [97,420,421]. В среднем интервал между инъекциями составляет 5 месяцев. В большинстве исследований инъекции выполняют в круговую мышцу глаза и круговую мышцу рта [418,422]. Получить оптимальный клинический эффект при лечении синкинезий позволяет химическая денервация нижней порции пальпебральной части круговой мышцы глаза, щечной мышцы, мышц периназальной области, подкожной мышцы шеи [101,423–425]. Нежелательными эффектами могут быть гематома, избыточная слабость инъецируемой мышцы или слабость соседней мышцы (диплопия/нарушение речи) [422]. Ботулинотерапия более эффективна на фоне проведения физической реабилитации [82].
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с гипертонусом мышц лица – здоровой стороны умеренной и выраженной степени при идиопатической и симптоматической НЛН [99].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Расслабление мышц лица проводят с условно здоровой стороны, в качестве дополнительного метода к стандартному комплексу лечебной физкультуры (который назначается в зависимости от выраженности пареза). В мышцы контрлатеральной стороны лица внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** и ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в общей дозе до 50 ЕД.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с гипертонусом мышц лица – пораженной стороны умеренной и выраженной степени (осложнение идиопатической и симптоматической НЛН) [101].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Расслабление мышц лица проводят с двух сторон, в качестве дополнительного метода к стандартному комплексу лечебной физкультуры (который назначается в зависимости от выраженности пареза) [101]. Марка препарата, доза, временной интервал и места инъекций выбираются [422]. В мышцы ипсилатеральной и контрлатеральной стороны лица внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** или ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в общей дозе до 100 ЕД.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с вторичным гемифациальным спазмом после идиопатической и симптоматической НЛН (постпаралитический гемиспазм) умеренной и выраженной степени [101].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Расслабление мышц лица проводят с двух сторон, в качестве дополнительного метода к стандартному комплексу лечебной физкультуры (который назначается в зависимости от выраженности пареза) [101]. Марка препарата, доза, временной интервал и места инъекций выбираются [422]. В мышцы ипсилатеральной и контрлатеральной стороны лица внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты ботулинический токсин типа А** или ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в общей дозе до 100 ЕД.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с гипертонусом мышц лица – здоровой стороны при поражении краевой нижнечелюстной ветви лицевого нерва с целью коррекции симметрии лица и создания условий для восстановления [426].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: инъекции выполняют на здоровой стороне в мышцу, опускающую нижнюю губу, внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** или ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** - в дозе 5 ЕД в одну точку [426] или в дозе по 2 ЕД в 2 точки [184].
Профилактика и лечение симптома лагофтальма и его осложнений
При НЛН одним из частых симптомов является лагофтальм – неполное смыкание век, который приводит к офтальмологическим осложнениям: кератиты, язвы роговицы, до потери органа зрения. Основные задачи:
восстановление целостности слезной пленки (увлажнение),
восстановление смыкания век – см. Медицинская реабилитация при НЛН, Приложение Б7 [102,119].
- Рекомендуется раннее назначение неврологом местной терапии – другие препараты, применяемые в офтальмологии, искусственные слезы и другие индифферентные препараты в разных формах (глазные капли, гели) для систематичного применения с частотой до нескольких раз в день и в ночное время пациентам с симптомом неосложнённого лагофтальма при НЛН с целью увлажнения глазного яблока и профилактики офтальмологических осложнений [427,428].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: наиболее частой схемой является назначение днем инстилляции капель искусственной слезы и других индифферентных препаратов (код АТХ – S01XA20) в соответствии с инструкцией; на ночь – декспантенол (код АТХ – S01XA12) в соответствии с инструкцией [102,119].
Хирургическое лечение
При НЛН метод хирургического лечения определяется сроком от дебюта симптомов, анатомическим уровнем (локализацией) повреждения, этиологией, степенью тяжести, клиническими проявлениями (выраженность дисфункции и деформации) (рисунок 8). Хирургическое лечение классифицируют на патогенетическое – направлено на устранение причины заболевания; симптоматическое – направлено на улучшение исхода (Приложение Б8).
У пациентов с НЛН при идиопатической форме патогенетическим хирургическим лечением является декомпрессия лицевого нерва в канале височной кости, которая проводится только в случаях тяжёлой степени поражения нерва, установленной клинически (V-VI степень по шкале ХБ) и подтвержденной инструментально (разница амплитуд М-волны пораженной и здоровой стороны более 90% по данным стимуляционной ЭНМГ). Пациентам с разницей амплитуд М-волны более 90% в обязательном порядке проводят ЭМГ с регистрацией ПДЕ. Отсутствие ПДЕ по данным ЭМГ расценивают как признак полного поражения ствола ЛН с неблагоприятным прогнозом спонтанного восстановления и, что является показанием к хирургическому лечению [429].
У пациентов с НЛН симптоматическим хирургическим лечением независимо от формы заболевания (идиопатическая или симптоматическая) являются реиннервирующая операция (невропластика) или реконструктивно-пластическая операция, которые проводят также только при тяжёлой степени поражения нерва (Приложение Б9) [177]. Хирургическое лечение (реиннервация мимических мышц) показано при отсутствии положительной динамики в течении 6 месяцев от дебюта симптомов и отсутствии динамики по данным миографии, может проводиться после патогенетического хирургического лечения.
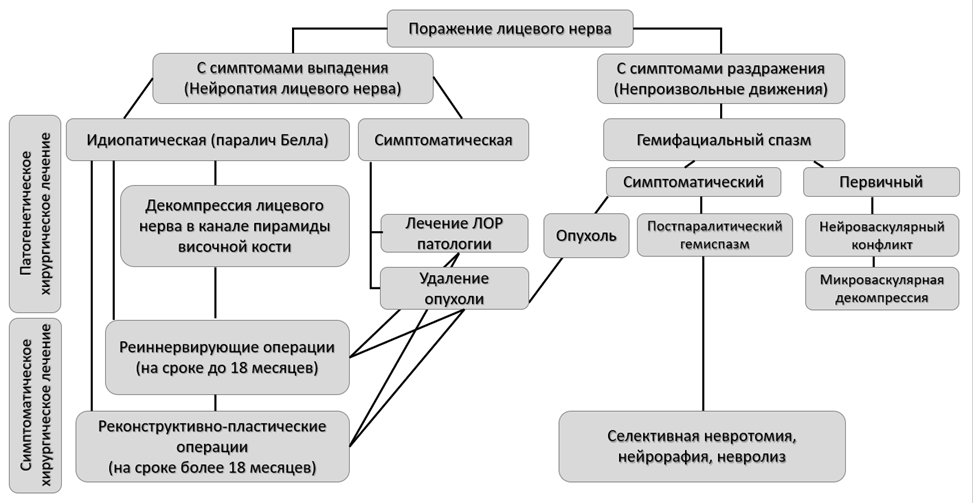
Рисунок 8. Хирургическое лечение пациентов с поражениями лицевого нерва
Суть реиннервирующих операций заключается в восстановлении функции мимических мышц путём восстановления анатомической целостности лицевого нерва (таблица 21). В случае отсутствия возможности восстановления анатомической целостности лицевого нерва требуется формирование периферических анастомозов между лицевым нервом (VII пара) и регионарными нервами в челюстно-лицевой области: подъязычный – VII пара, жевательный – V пара, а также перекрёстно лицевая реиннервация с использованием лицевого нерва со здоровой стороны. Срок проведения таких операций до 2 лет (оптимально – до 18 месяцев) от дебюта симптомов.
Суть реконструктивно-пластической операции заключается в двух этапном микрохирургическом лечении (мионевропластика), а именно первый этап заключается в заборе аутотрансплантата в донорской области (икроножный или поверхностный малоберцовый нерв) и в проведении со здоровой стороны на поражённую. Особенность операции заключается в подготовке реципиентного нерва для реиннервации пересаживаемой мышцы. Необходимо соблюдать правила восстановления анатомической и функциональной целостности зоны иннервации, делая акцент на формирование миодинамического равновесия. Хирургическое лечение пациентов с тяжёлой НЛН является основополагающим, но только комплексный подход, своевременно и планомерно осуществляемая специализированная помощь позволяет обеспечить пациентам оптимальный функциональный и эстетический эффект лечения и полную реабилитацию [82,177,430].
Таблица 21. Категории пациентов и виды симптоматического хирургического лечения при поражении лицевого нерва
Идиопатическая и симптоматическая форма нейропатии лицевого нерва | Вид хирургического лечения | Цель хирургического лечения |
|---|
тяжёлой степени со сроком заболевания до 18 месяцев | Реиннервирующие операции | Восстановление функции собственных мимических мышц |
тяжёлой степени со сроком заболевания более 18 месяцев | Реконструктивно-пластические операции (аутотрансплантация мышцы) | Замещение функций атрофированных мимических мышц |
постпаралитический гемиспазм (выраженные синкинезии) | Селективная невротомия, селективная нейрорафия, невролиз, | Формирование естественной улыбки путём разобщения движений между несколькими групп мышц |
лагофтальм | Хирургическое лечение лагофтальма (нейропластические, динамические и статические методы) | Восстановление функции круговой мышцы глаза, имитация функции круговой мышцы глаза |
Идиопатическая нейропатия лицевого нерва (паралич Белла)
- Рекомендуется проведение невролиза и декомпрессии лицевого нерва (декомпрессии лабиринтного сегмента лицевого нерва) пациенту с идиопатической НЛН и тяжелой степенью его поражения для улучшения исхода заболевания [92,209].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: Операция требует тщательного отбора пациентов. Диагноз паралич Белла должен быть достоверно установлен на основании комплексной клинико-инструментальной оценки, а именно тяжесть повреждения по данным шкалы ХБ должна соответствовать V-VI степени, по данным стимуляционной ЭНМГ разница амплитуд М-волны пораженной и здоровой стороны должна превышать 90%, исключены рецидивирующие нейропатии и исключены другие причины повреждения лицевого нерва [92] (УДД - 1). Хирургическую декомпрессию лицевого нерва рекомендуют выполнять в течение 14 дней, предпочтительно – через среднюю черепную ямку в сравнении с трансмастоидным доступом [209] (УДД - 1). Однако, операция требует тщательного отбора пациентов и предоперационной подготовки, что занимает время. Проведение хирургической декомпрессии возможно на сроке до 3 месяцев от дебюта симптомов [210–212]. В случае положительной динамики за это время (клинической или миографической) хирургическое лечение не проводят.
- Рекомендуется проведение компьютерной томографии височной кости пациентам с клинической картиной НЛН перед проведением невролиза и декомпрессии лицевого нерва (декомпрессии лабиринтного сегмента лицевого нерва) с целью оценки анатомических ориентиров пирамиды височной кости и предоперационного планирования хирургического доступа [431].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение тональной аудиометрии пациентам с клинической картиной НЛН перед проведением невролиза и декомпрессии лицевого нерва (декомпрессии лабиринтного сегмента лицевого нерва) с целью оценки слуха [212,431,432].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: риск потери слуха ипсилатерально при данном виде хирургического вмешательства составляет 2-5% [212].
Идиопатическая или симптоматическая нейропатия лицевого нерва
- Рекомендуется проведение реиннервирующей операции (нейрорафии) пациенту с НЛН и тяжелой степенью его поражения после 3 месяцев от дебюта симптомов до 2 лет (оптимально – до 18 месяцев) с целью улучшения исхода заболевания [213,214,220–226].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: Тяжесть поражения лицевого нерва устанавливается на основании комплексной клинико-инструментальной оценки, а именно тяжесть повреждения по данным шкалы ХБ должна соответствовать V-VI степени, по данным стимуляционной ЭНМГ разница амплитуд М-волны пораженной и здоровой стороны должна превышать 90%. Учитывается наличие или отсутствие атрофии мышц по данным УЗИ или МРТ.
- Рекомендуется проведение реконструктивно-пластической операции (свободной пересадки или перемещения донорских мышц путём аутотрансплантации) пациенту с НЛН и тяжелой степенью его поражения после 2 лет от дебюта симптомов с целью улучшения исхода заболевания [215–219,227].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: Тяжесть поражения лицевого нерва устанавливается на основании комплексной клинико-инструментальной оценки, а именно тяжесть повреждения по данным шкалы ХБ должна соответствовать V-VI степени, по данным стимуляционной ЭНМГ разница амплитуд М-волны пораженной и здоровой стороны должна превышать 90%. Учитывается наличие или отсутствие атрофии мышц по данным УЗИ или МРТ.
- Рекомендуется проведение невролиза, нейрорафии, невротомии или миотомии пациенту с последствием НЛН – выраженным постпаралитическим гемиспазмом (множественные синкинезии) с целью устранения непроизвольных движений [228–230].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: с учетом побочных эффектов в виде слабости мышц лица требуется тщательный отбор пациентов.
Методы хирургического лечения пациентов с прозоплегией
- Рекомендуется проведение нейрорафии XII-VII черепных нервов «бок в конец» с использованием вставки из большого ушного нерва, «конец в конец» с использованием челюстно-подъязычной ветви или «конец в конец» с использованием жевательной ветви пациентам с НЛН вследствие интракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва давностью до 2 лет и прозоплегией мышц с целью «скорой помощи» в восстановлении проводимости лицевого нерва на периферическом уровне за счёт донорского нерва [213,214,220].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение нейрорафии XII-VII черепных нервов «конец в конец» с использованием икроножного нерва или «конец в конец» с использованием икроножного нерва по типу мионевротизации пациентам с НЛН с отсутствием симметричных синхронных движений с целью синхронизации и усиления движений мимической мускулатуры за счёт не поврежденной стороны лица [220,433–435].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение нейрорафии XII-VII черепных нервов «бок в конец» с использованием вставки из большого ушного нерва, «конец в конец» с использованием жевательной ветви или периферический анастомоз V-VII черепных нервов «конец в конец» с использованием челюстно-подъязычной ветви пациентам с НЛН вследствие экстракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва с сохранением ствола и ветвей давностью до 2 лет и прозоплегией с целью «скорой помощи» в восстановлении проводимости лицевого нерва на периферическом уровне за счёт донорского нерва [213,214,220–226].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций СВ (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение ревизии ствола и ветвей лицевого нерва с формированием вставок из большого ушного и/или икроножного нервов (прямая нейрорафия) или проведение нейрорафии XII-VII черепных нервов «бок в конец» с использованием вставок из икроножного и/или большого ушного нервов или «конец в конец» с использованием жевательной ветви и вставок из большого ушного и/или икроножного нервов пациентам с НЛН вследствие экстракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва без сохранения ствола и ветвей давностью до 2 лет и прозоплегией с целью «скорой помощи» в восстановлении проводимости лицевого нерва на периферическом уровне за счёт донорского нерва [213,214,220–226].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение свободной пересадки или перемещения донорских мышц путём аутотрансплантации с одномоментной реиннервацией жевательной ветвью тройничного нерва с кросс-пластикой или транспозиции жевательных мышц с одномоментной реиннервацией с кросс-пластикой пациентам с НЛН вследствие интракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва давностью более 2 лет, прозоплегией и атрофией мимических мышц с целью восстановления статической симметрии лица [215–219,227].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение статической коррекции с использованием бедренной и/или височной фасции пациентам с НЛН вследствие интракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва давностью более 2 лет, прозоплегией и атрофией мимических мышц в случаях, когда свободная пересадка или перемещение донорских мышц невозможно [216,436].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: в случаях противопоказаний к хирургическому лечению или при отказе пациента возможна статическая коррекция с использованием нитей.
Методы хирургического лечения пациентов с прозопарезом
- Рекомендуется проведение нейрорафии XII-VII черепных нервов «бок в бок» с использованием вставки из большого ушного нерва, нейрорафии V-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием челюстно-подъязычной ветви или жевательной ветви, нейрорафии VII-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием икроножного нерва или нейрорафии в сочетании с мионевратизацией пациентам с НЛН вследствие интракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва с целью «скорой помощи» в усилении проводимости лицевого нерва на периферическом уровне за счёт донорского нерва [220,434,435].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение ревизии ствола и ветвей лицевого нерва (невролиз, нейрорафия), нейрорафии VII-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием икроножного нерва или икроножного нерва по типу мионевротизации, ревизии ствола и ветвей лицевого нерва с формированием вставок из большого ушного и/или икроножного нервов (прямая нейрорафия) или комбинация различных видов нейрорафий с кросспластикой пациентам с НЛН вследствие экстракраниального повреждения лицевого нерва с целью восстановления анатомо-функциональной целостности лицевого нерва [220,433–435].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение селективной миотомии на здоровой половине лица, нейрорафии VII-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием икроножного нерва или икроножного нерва по типу мионевротизации, селективной нейротомии на здоровой половине лица с использованием интраоперационного мониторинга лицевого нерва пациентам с НЛН и контрактурами здоровой стороны лица с целью временного устранения гипертонуса мимической мускулатуры с учётом прорастания сформированных нейрорафий [423,433,435,437].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение нейрорафии VII-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием икроножного нерва по типу мионевротизации, селективной нейротомии с использованием интраоперационного мониторинга лицевого нерва, селективной миотомии, нейрорафии VII-VII черепных нервов «конец в бок» с использованием икроножного нерва пациентам с НЛН и контрактурами и синкинезиями пораженной стороны лица с целью устранения контрактуры и разобщения содружественных движений мимической мускулатуры [77,423,433–435,437].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Рекомендуется проведение статической коррекции с использованием полосок из височной и/ или бедренной фасций или статическая коррекция по типу круговой подтяжки лица пациентам с НЛН и прозопарезом с целью временной коррекции птоза тканей в эстетических целях [423,433,436,437].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Методы хирургического лечения пациентов с паралитическим лагофтальмом
- Рекомендуется устранение ретракции верхнего века и лагофтальма различной степени выраженности пациентам с постпаралитическим лагофтальмом давностью более 2 лет с целью восстановления смыкания век [216,438].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Методы лечения паралитического лагофтальма включают: имплантацию золотого грузика в верхнее веко, кожно – хрящевой лоскут с ушной раковины, латеральную и медиальную кантопексию с использованием височной фасции и/ или ушного хряща, блефарорафию, устранение ретракции верхнего века с использованием височной фасции, устранение ретракции верхнего века с использованием ушного хряща, латеральную и медиальную кантопексию.
3.2.2. Гемифациальный спазм
Медикаментозное лечение
- Рекомендуется применение препаратов #карбамазепин** (код АТХ – N03AF01), #габапентин (код АТХ – N03AX12), #клоназепам** (код АТХ – N03AE01); #диазепам** (код АТХ – N05BA01), #лоразепам** (код АТХ – N05BA06), #баклофен** (код АТХ – M03BX01), #леветирацетам** (код АТХ – N03AX14), #зонисамид** (код АТХ – N03AX15) пациентам с гемифациальным спазмом при отсутствии показаний к хирургическому лечению, наличии противопоказаний к нему или при отказе пациента от операции, а также в случаях неэффективности ботулинотерапии с целью облегчения симптомов спазма [439–441].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Представленные препараты обладают недоказанной эффективностью в снятии спазма, имеют побочные эффекты в виде чрезмерной седации, утомляемости. Стандартная доза для применения препаратов составляет: #карбамазепин** 400-1200 мг в сутки, #габапентин 600-1200 мг в сутки, #клоназепам** 0,5-4 мг в сутки, другие бензодиазепины (#диазепам** и #лоразепам**) в эквивалентных дозах, #баклофен** 15-80 мг в сутки, #леветирацетам** 500-1500 мг в сутки, #зонисамид** 150 мг 2 раза в сутки в течение 6 недель [440,441].
Ботулинотерапия
При первичном и вторичном гемифациальном спазме лечением первой линии является назначение ботулинического токсина, что подтверждено множеством клинических исследований [15]. Ботулинотерапия при ГФС обладает симптоматическим и патофизиологическим механизмами действия. С одной стороны, блокируя нервно-мышечную передачу, инъекции подавляют миоклонические гиперкинезы. С другой стороны, подавляя гиперактивность мышц, ботулинотерапия препятствует формированию гипервозбудимости, сенситизации и нейропластичности ядерного и надъядерного уровней иннервации мышц лица. Исходя из этих обстоятельств, инъекции БТА следует назначать на этапах минимальных проявлений спазма и малой продолжительности заболевания [15]. Инъекции выполняют в мышцы лица с двух сторон с целью не только уменьшения клинических проявлений спазма, но и улучшения симметрии [442,443]. Мышцами-мишенями при ГФС являются круговая мышца глаза, щечная мышца, подкожная мышца шеи. При выполнении инъекций в скуловые мышцы высокий риск развития асимметрии улыбки, в круговую мышцу рта – прикус губ, нарушение речи и приёма пищи [15]. У 76-100% пациентов с ГФС клиническое улучшение наступает в течение 7 дней после введения препарата с продолжительностью эффекта до 90 дней, рекомендуемый интервал между инъекциями от 3 месяцев [15].
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с гемифациальным спазмом (первичным, вторичным, идиопатическим) с целью уменьшения его клинических проявлений и улучшения симметрии лица [442–444].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: В мышцы ипсилатеральной и контрлатеральной стороны лица внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты ботулинический токсин типа А** и ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в общей дозе до 100 ЕД.
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с гемифациальным спазмом при возврате симптомов ГФС после васкулярной декомпрессии с целью уменьшения его клинических проявлений и улучшения симметрии лица [445,446].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: В мышцы ипсилатеральной и контрлатеральной стороны лица внутримышечно вводят ботулинический токсин (код АТХ – M03AX01) – препараты ботулинический токсин типа А** и ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс** в общей дозе до 100 ЕД.
Хирургическое лечение
У пациентов с первичным гемифациальным спазмом при наличии подтвержденного НВК по данным МРТ проводят васкулярную декомпрессию как единственный патогенетически обоснованный метод лечения, суть операции заключается в разобщении сосуда и нерва (Приложение Б10) [49].
У пациентов с вторичным гемифациальным спазмом вид оперативного вмешательства определяет его причина. Так, при компрессии нерва объемным образованием – удаление объемного образования (патогенетическое лечение). Если гемифациальный спазм развился после перенесенной НЛН для уменьшения выраженности спазма проводят селективную невротомию, селективную нейрорафию, невролиз (симптоматическое лечение) – см. хирургическое лечение при нейропатии лицевого нерва.
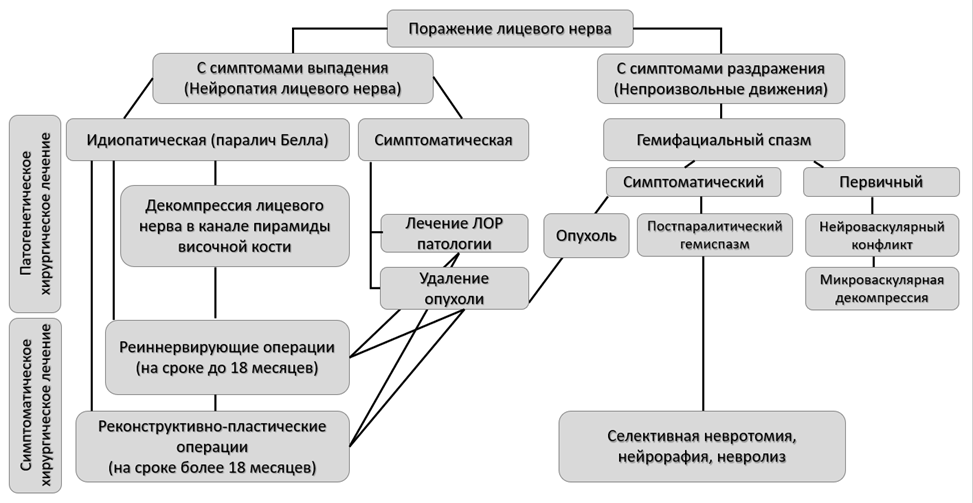
Рисунок 8. Хирургическое лечение пациентов с поражениями лицевого нерва
- Рекомендуется проведение декомпрессии корешка черепно-мозгового нерва (лицевого) пациентам с первичным ГФС при подтверждении НВК по данным МРТ с целью разобщения сосуда и нерва [231,232].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
Комментарии: Противопоказаниями к хирургическому лечению являются: тяжелая сопутствующая патология, препятствующая проведению хирургического вмешательства или отказ пациента от хирургического вмешательства [49]. При наблюдении за пациентами в течение 1 года излечение наступило у более 90% пациентов [231].
- Рекомендуется при проведении декомпрессии корешка черепно-мозгового нерва (лицевого) пациентам с первичным ГФС использовать интраоперационный мониторинг Lateral Spread Recording с целью улучшения результатов операций [447].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1)
- Рекомендуется рассмотреть возможность проведения радиохирургического лечения (стереотаксически ориентированное дистанционное лучевое лечение) пациентам с первичным и идиопатическим ГФС в случаях, когда хирургическое лечение открытым доступом не показано, противопоказано или пациент от него отказывается, при сохранении симптомов после проведенного лечения, а также при неэффективности лечения ботулиническим токсинам и другими медикаментами [448].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
- Комментарии: мишенью при радиохирургическом лечении является лицевой нерв на участке непосредственно перед его входом во внутреннее слуховое отверстие. Рекомендуемая доза 8 Гр однократно или 15 Гр в 5 фракциях по 3 Гр каждая.
3.2.3. Лицевая миокимия
Медикаментозное лечение
- Рекомендуется физический и эмоциональный покой, снижение потребления кофеина, устранение провоцирующих факторов пациентам с первичной лицевой миокимией с целью купирования спазма [16].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: Первичная лицевая миокимия проходит в течение нескольких дней или недель при отдыхе и устранении провоцирующих факторов (курение, употребление алкоголя и кофеина). При вторичной лицевой миокимии проводят лечение основного заболевания.
Ботулинотерапия
- Рекомендуется назначение ботулинического токсина при заболеваниях периферической нервной системы пациентам с лицевой миокимией, продолжающейся более 3 месяцев c целью уменьшения клинических симптомов [16].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Комментарии: при лицевой миокимии, продолжающейся более 3 месяцев в первую очередь необходимо исключить другие причины поражения лицевого нерва. Лечение инъекциями БТА является симптоматическим. Однократно или при необходимости повторно вводят 5-20 ЕД БТА в мышцу с гиперкинезом (при миокимии века – в круговую мышцу глаза). Используют препараты #ботулинический токсин типа А** и #ботулинический токсин типа А-гемагглютинин комплекс**.
Хирургическое лечение
Хирургическое лечение не предусмотрено.
3.3. Поражения других черепных нервов
- Рекомендованы три подхода к лечению: консервативная терапия, малоинвазивные интервенции и хирургические вмешательства [79,80]. Консервативное лечение включает в себя профилактическую терапию и купирование приступов острой боли.
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Консервативная терапия
Профилактическое лечение лекарственными препаратами
- Рекомендуется прием #Карбамазепина** (код АТХ - N03AF01) пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва для профилактического лечения [449].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: препарат назначают по правилам дозирования при тригеминальной невралгии, средняя терапевтическая доза у пациентов с невропатией языкоглоточного нерва 100-2000 мг в сутки..
- Рекомендуется прием #Окскарбазепина** (код АТХ - N03AF02) пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва для профилактического лечения [450].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: препарат следует назначать с 300 мг в сутки с постепенным увеличением до 1200 мг в сутки.
- Рекомендуется прием #Габапентина (код АТХ - N02BF01, N03AX12) пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва для профилактического лечения [449].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: препарат назначают по правилам дозирования при тригеминальной невралгии, средняя терапевтическая доза у пациентов с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва 100-5000 мг в сутки.
Общие рекомендации по ведению пациентов с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва включают:
При выборе препарата следует учитывать противопоказания к применению, индивидуальную переносимость. Для улучшения переносимости лечения возможно менять препарат на дженерик с аналогичным действующим веществом и дозой;
Для оценки переносимости лечение следует начинать с монотерапии. При необходимости назначения комбинированной терапии следует назначать препараты поочередно для оценки переносимости каждого.
Иное профилактическое лечение
- Рекомендуется выполнение инъекций #ботулинического токсина типа А** или #ботулинического токсина типа А – гемагглютинин комплекс** (код АТХ - M03AX01) пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва в качестве дополнительного профилактического лечения по 1,25-5 ЕД внутрикожно в перикраниальные мышцы и мышцы шеи до 25-100 ЕД [451].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Малоинвазивная интервенция у пациентов с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва
Малоинвазивная интервенция у пациентов с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва
- Рекомендуется проведение радиочастотной абляции периферических нервов, сплетений, вегетативных ганглиев в объеме импульсной радиочастотной абляции языкоглоточного нерва под КТ или ультразвуковым контролем пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва [452]
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
- Рекомендуется проведение блокады языкоглоточного нерва в проекции шиловидного отростка под КТ или ультразвуковым контролем пациентам с невралгией языкоглоточного нерва [453].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств - 3)
Хирургическое лечение
Хирургическое вмешательство рассматривается при фармакорезистентном течении болевого синдрома и нарушении качество жизни пациента. Необходимо своевременно информировать пациента о возможностях хирургического лечения и направлять пациента в нейрохирургический центр.
Хирургическое лечение необходимо проводить в специализированных нейрохирургических отделениях с опытом проведения операций на головном мозге и при невралгии языкоглоточного нерва
- Рекомендуется нейрохирургическое лечение в объеме микроваскулярной декомпрессии корешка языкоглоточного нерва пациентам с фармакорезистентным течением первичной невралгии языкоглоточного нерва [234,454,455].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Проводилось сравнительное исследование эффективности микроваскулярной декомпрессии корешка языкоглоточного нерва и микроваскулярной декомпрессии с одновременным выполнением ризотомии. Не было найдено статистически значимых различий в отношении контроля болевого синдрома и осложнений [456].
- Рекомендуется проведение стереотаксической операции на головном мозге – облучение корешка языкоглоточного нерва пациентам с идиопатической или классической НЯН в случае невозможности проведения микроваскулярной декомпрессии, в том числе при отказе пациента от хирургического лечения [457].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарий: Предпочтительным является облучение на аппарате «Гамма-нож», также допустимо проведение лечения на линейных ускорителях с возможностью проведения стереотаксической радиохирургии.
- Рекомендуется проведение ризотомии (микрохирургической частичной (сенсорной) ризотомии) корешка языкоглоточного нерва в случае невозможности проведения микроваскулярной декомпрессии с целью уменьшения интенсивности болевого синдрома [458].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
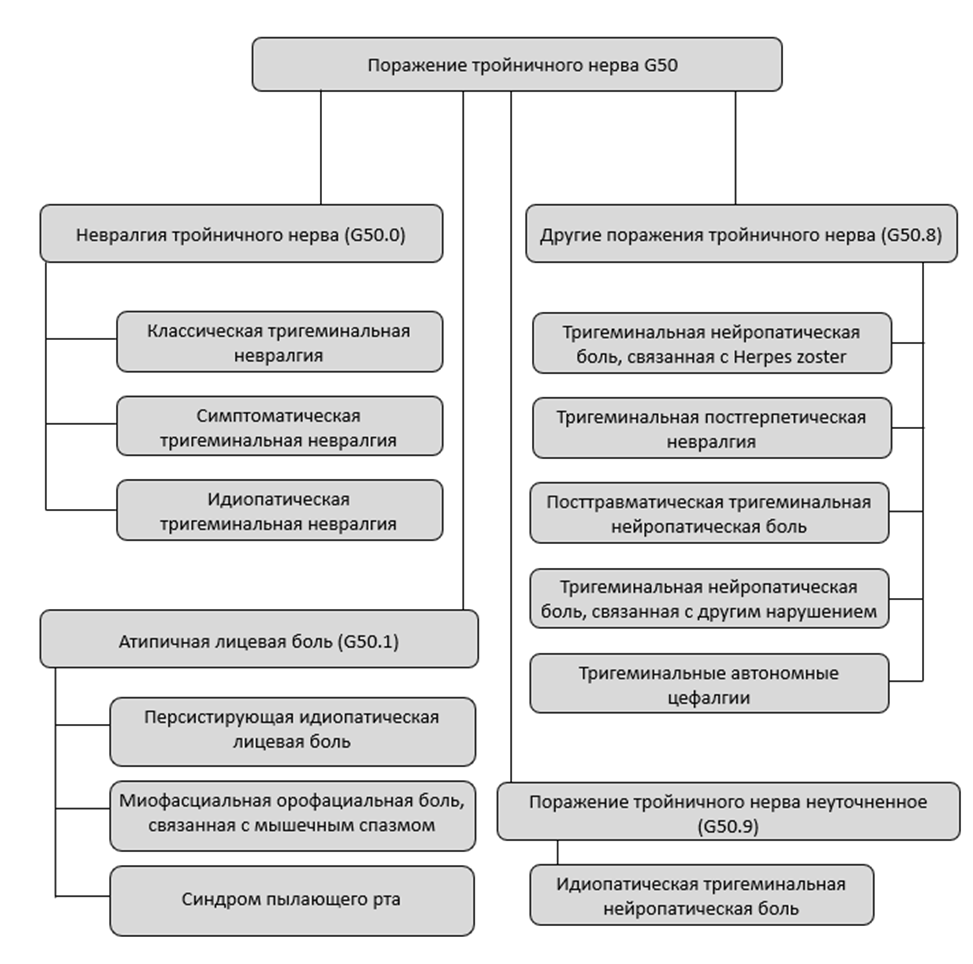
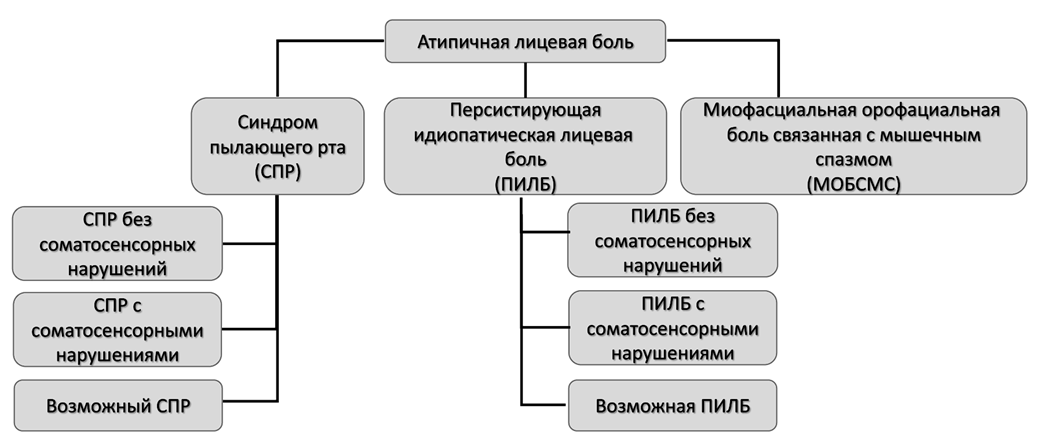
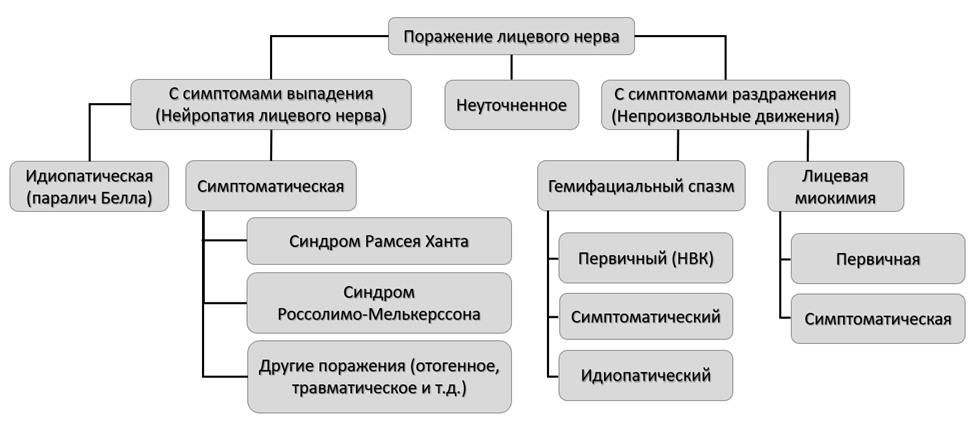
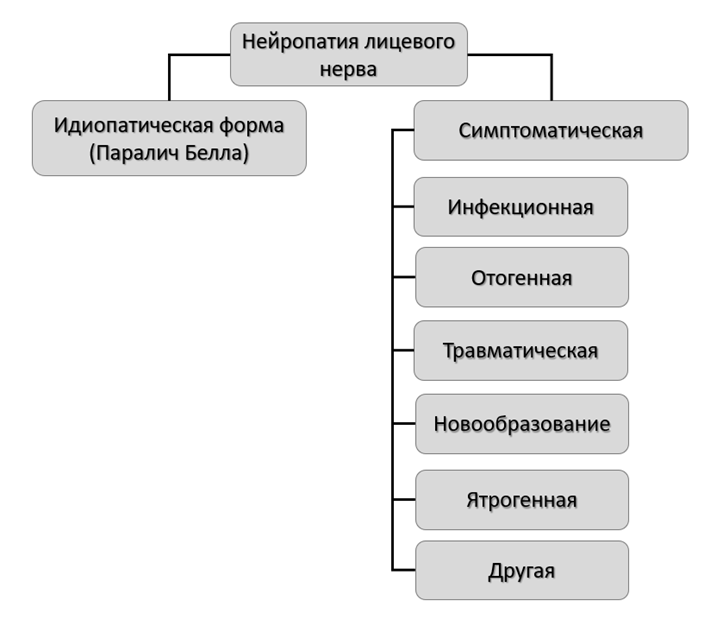
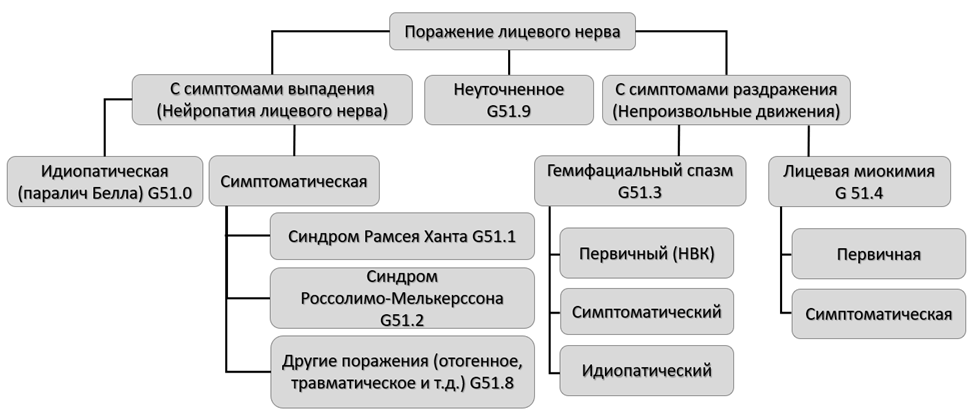


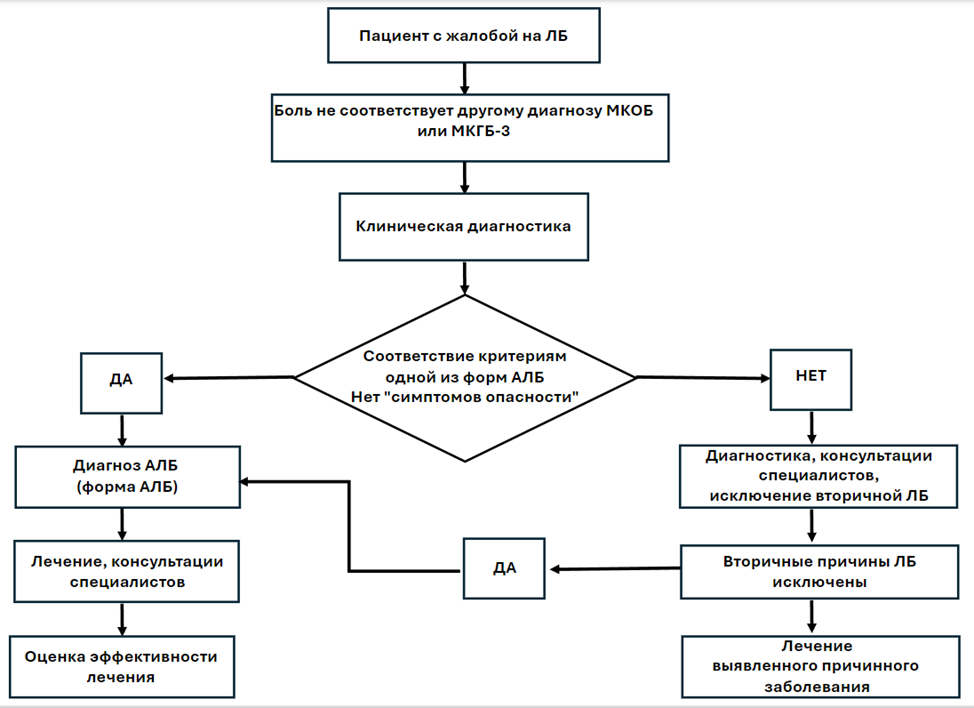
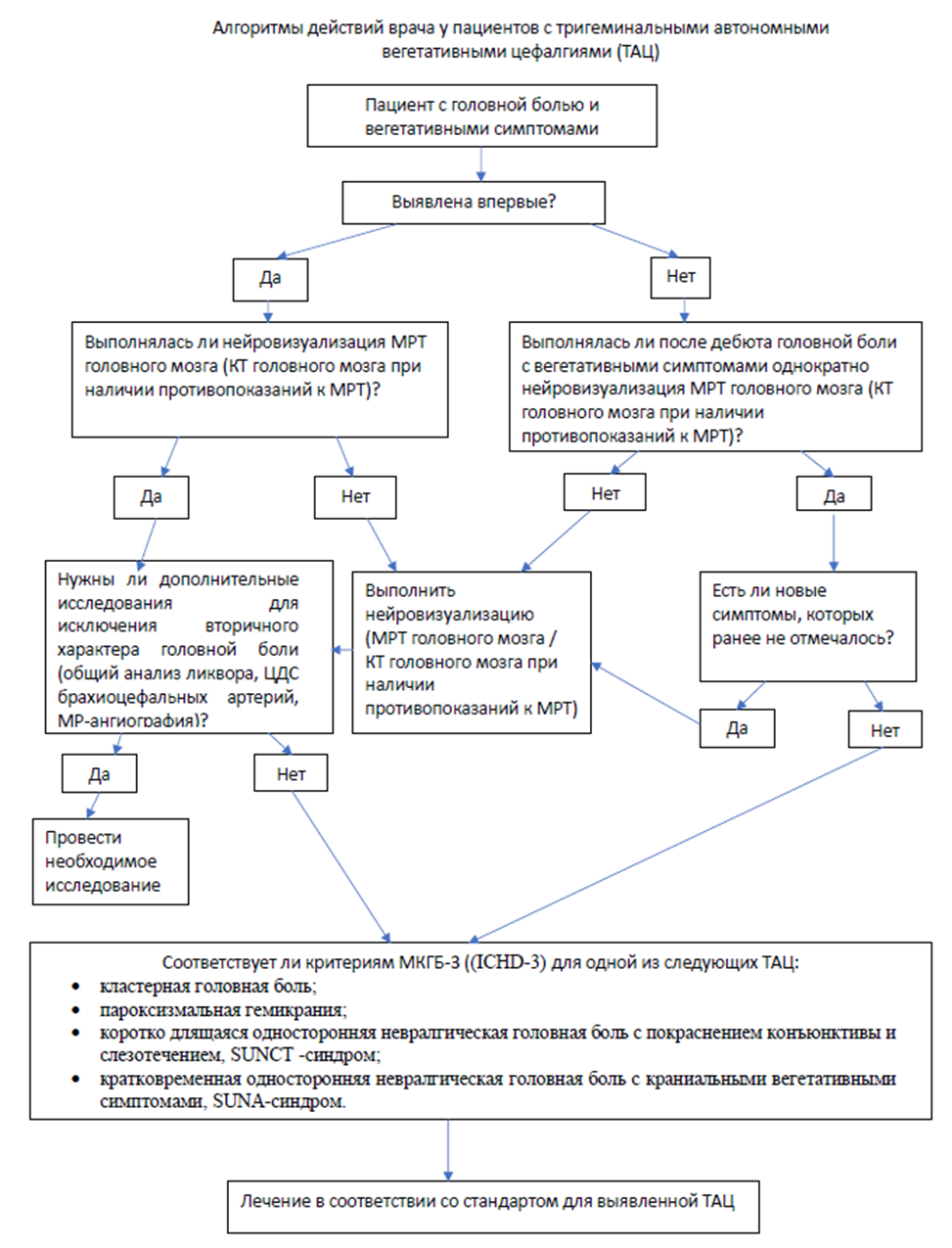
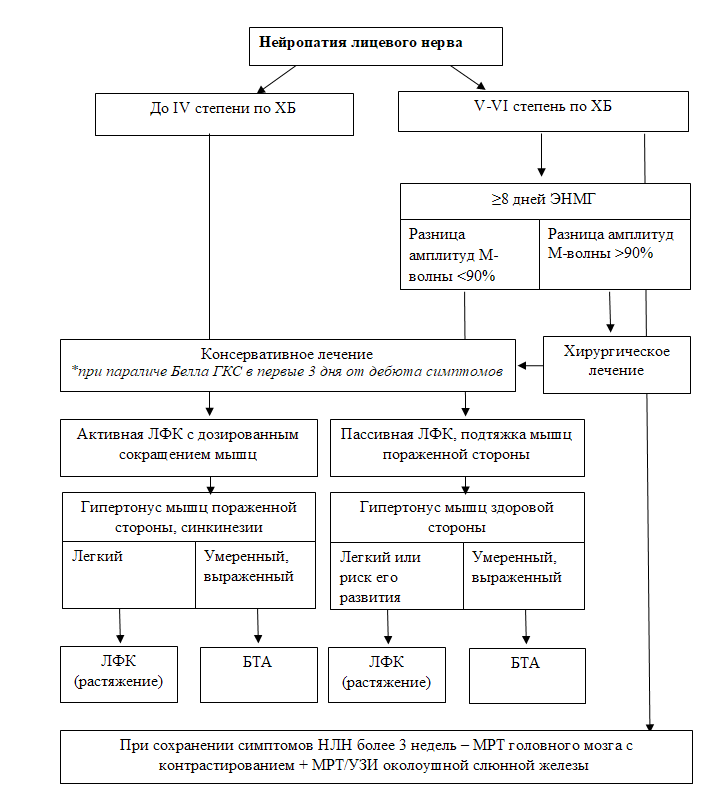
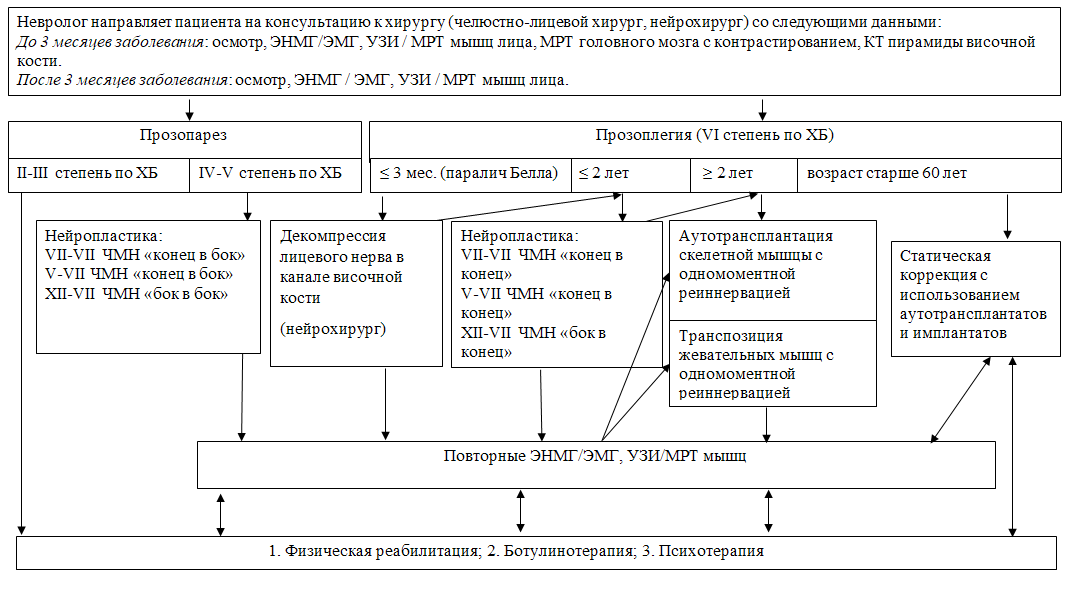 Приложение Б9.
Приложение Б9.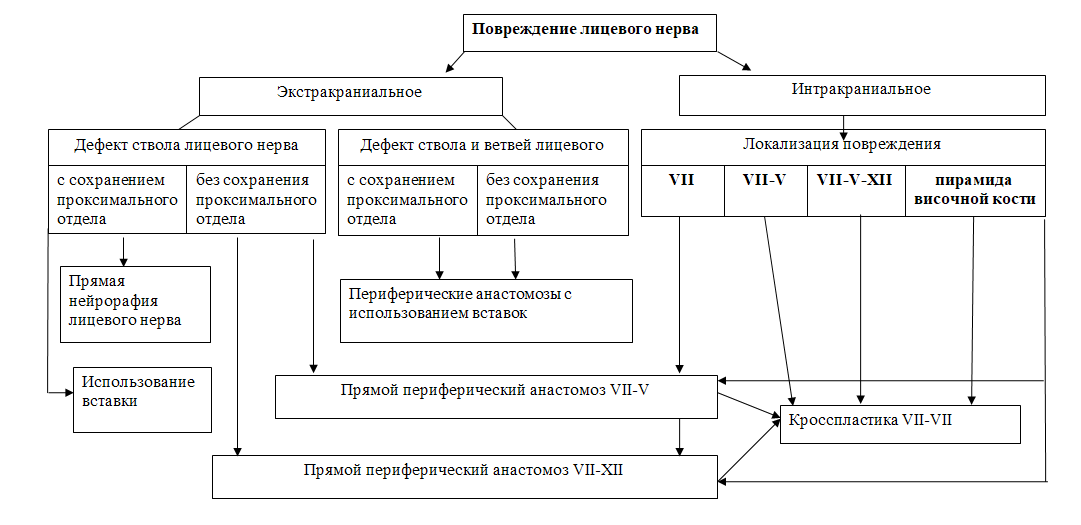 Приложение Б10
Приложение Б10